Bone
1. Aguirre JI'' Plotkin LI'' Gortazar AR'' Millan MM'' O’Brien CA'' Manolagas SC'' Bellido T. A novel ligand-independent function of the estrogen receptor is essential for osteocyte and osteoblast mechanotransduction. J Biol Chem 282(35):25501–25508'' 2007.
2. Bellido T'' Plotkin LI. Detection of apoptosis of bone cells in vitro. Methods in Molecular Biology'' Vol. 455: Osteoporosis: Methods and Protocols. Edited by Westendorf JJ. Humana Press: Totowa'' 51-75'' 2008.
3. Bhatt KA'' Chang EI'' Warren SM'' Lin SE'' Bastidas N'' Ghali S'' Thibboneir A'' Capla JM'' McCarthy JG'' Gurtner GC. Uniaxial mechanical strain: an in vitro correlate to distraction osteogenesis. J Surg Res 143(2):329-36'' 2007. Epub 2007 Oct 22.
4. Boutahar N'' Guignandon A'' Vico L'' Lafage-Proust MH. Mechanical strain on osteoblasts activates autophosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase and proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 tyrosine sites involved in ERK activation. J Biol Chem 279(29):30588-30599'' 2004.
5. Buckley MJ'' Banes AJ'' Jordan RD. The effects of mechanical strain on osteoblasts in vitro. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 48(3):276-282'' 1990.
6. Buckley MJ'' Banes AJ'' Levin LG'' Sumpio BE'' Sato M'' Jordan R'' Gilbert J'' Link GW'' Tran Son Tay R. Osteoblasts increase their rate of division and align in response to cyclic'' mechanical tension in vitro. Bone Miner 4(3):225-236'' 1988.
7. Calvalho RS'' Bumann A'' Schwarzer C'' Scott E'' Yen EH. A molecular mechanism of integrin regulation from bone cells stimulated by orthodontic forces. Eur J Orthod 18(3):227-235'' 1996.
8. Carvalho RS'' Bumann A'' Schwarzer C'' Scott E'' Yen HK. A molecular mechanism of integrin regulation from bone cells stimulated by orthodontic forces. The European Journal of Orthodontics 18(1):227-235'' 1996.
9. Carvalho RS'' Scott JE'' Suga DM'' Yen EH. Stimulation of signal transduction pathways in osteoblasts by mechanical strain potentiated by parathyroid hormone. J Bone Miner Res 9(7):999-1011'' 1994.
10. Carvalho RS'' Scott JE'' Yen EH. The effects of mechanical stimulation on the distribution of β1 integrin and expression of β1-integrin mRNA in TE-85 human osteosarcoma cells. Arch Oral Biol 40(3):257-264'' 1995.
11. Case N'' Ma M'' Sen B'' Xie Z'' Gross TS'' Rubin J. β-catenin levels influence rapid mechanical responses in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem 283(43):29196-29205'' 2008. Epub 2008 Aug 22.
12. Chen X'' Macica CM'' Ng KW'' Broadus AE. Stretch-induced PTH-related protein gene expression in osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Res 20(8):1454-61'' 2005.
13. Cillo JE Jr'' Gassner R'' Koepsel RR'' Buckley MJ. Growth factor and cytokine gene expression in mechanically strained human osteoblast-like cells: implications for
distraction osteogenesis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 90(2):147-154'' 2000.
14. Duncan RL'' Hruska KA. Chronic'' intermittent loading alters mechanosensitive channel characteristics in osteoblast-like cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 267:F909-F916'' 1994.
15. Fan X'' Rahnert JA'' Murphy TC'' Nanes MS'' Greenfield EM'' Rubin J. Response to mechanical strain in an immortalized pre-osteoblast cell is dependent on ERK1/2. J Cell Physiol 207(2):454-460'' 2006.
16. Faure C'' Linossier MT'' Malaval L'' Lafage-Proust MH'' Peyroche S'' Vico L'' Guignandon A. Mechanical signals modulated vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) alternative splicing in osteoblastic cells through actin polymerisation. Bone 42(6):1092-1101'' 2008. Epub 2008 Feb 29.
17. Faure C'' Vico L'' Tracqui P'' Laroche N'' Vanden-Bossche A'' Linossier MT'' Rattner A'' Guignandon A. Functionalization of matrices by cyclically stretched osteoblasts through matrix targeting of VEGF. Biomaterials 31(25):6477-6484'' 2010. Epub 2010 Jun 11.
18. Geng WD'' Boskovic G'' Fultz ME'' Li C'' Niles RM'' Ohno S'' Wright GL. Regulation of expression and activity of four PKC isozymes in confluent and mechanically stimulated UMR-108 osteoblastic cells. J Cell Physiol 189(2):216-228'' 2001.
19. Granet C'' Boutahar N'' Vico L'' Alexandre C'' Lafage-Proust MH. MAPK and SRC-kinases control EGR-1 and NF-κB inductions by changes in mechanical environment in osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284(3):622-631'' 2001.
20. Granet C'' Vico AG'' Alexandre C'' Lafage-Proust MH. MAP and src kinases control the induction of AP-1 members in response to changes in mechanical environment in osteoblastic cells. Cellular Signaling 14(8):679-688'' 2002.
21. Grimston SK'' Screen J'' Haskell JH'' Chung DJ'' Brodt MD'' Silva MJ'' Civitelli R. Role of connexin43 in osteoblast response to physical load. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1068:214-224'' 2006.
22. Guignandon A'' Akhouayri O'' Usson Y'' Rattner A'' Laroche N'' Lafage-Proust MH'' Alexandre C'' Vico L. Focal contact clustering in osteoblastic cells under mechanical stresses: microgravity and cyclic deformation. Cell Commun Adhes 10(2):69-83'' 2003.
23. Guignandon A'' Boutahar N'' Rattner A'' Vico L'' Lafage-Proust MH. Cyclic strain promotes shuttling of PYK2/Hic-5 complex from focal contacts in osteoblast-like cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 343(2):407-14'' 2006.
24. Hara F'' Fukuda K'' Asada S'' Matsukawa M'' Hamanishi C. Cyclic tensile stretch inhibition of nitric oxide release from osteoblast-like cells is both G protein and actin-dependent. Journal of Orthopaedic Research 19(1):126-131'' 2001.
25. Hara F'' Fukuda K'' Ueno M'' Hamanishi C'' Tanaka S. Pertussis toxin-sensitive G proteins as mediators of stretch-induced decrease in nitric-oxide release of osteoblast-like cells. J Orthop Res 17(4):593-597'' 1999.
26. Hens JR'' Wilson KM'' Dann P'' Chen X'' Horowitz MC'' Wysolmerski JJ. TOPGAL mice show that the canonical Wnt signaling pathway is active during bone development and growth and is activated by mechanical loading in vitro. J Bone Miner Res 20(7):1103-1113'' 2005.
27. Ho AM'' Marker PC'' Peng H'' Quintero AJ'' Kingsley DM'' Huard J. Dominant negative Bmp5 mutation reveals key role of BMPs in skeletal response to mechanical stimulation. BMC Dev Biol 8:35'' 2008.
28. Jansen JH'' Weyts FA'' Westbroek I'' Jahr H'' Chiba H'' Pols HA'' Verhaar JA'' van Leeuwen JP'' Weinans H. Stretch-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2 depends on differentiation stage of osteoblasts. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 93:542–551'' 2004.
29. Kim DW'' Lee HJ'' Karmin JA'' Lee SE'' Chang SS'' Tolchin B'' Lin S'' Cho SK'' Kwon A'' Ahn JM'' Lee FY. Mechanical loading differentially regulates membrane-bound and soluble RANKL availability in MC3T3-E1 cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1068:568-72.'' 2006.
30. Knoll B'' McCarthy TL'' Centrella M'' Shin J. Strain-dependent control of transforming growth factor- β function in osteoblasts in an in vitro model: biochemical events associated with distraction osteogenesis. Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery 116(1):224-233'' 2005.
31. Li L'' Chen M'' Deng L'' Mao Y'' Wu W'' Chang M'' Chen H. The effect of mechanical stimulation on the expression of α2'' β1'' β3 integrins and the proliferation'' synthetic function in rat osteoblasts. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi 20(2):187-192'' 2003.
32. Li L'' Deng L'' Chen M'' Wu W'' Mao Y'' Chen H. The effect of mechanical stimulation on the proliferation and synthetic function of osteoblasts from osteoporotic rat. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi 21(3):341-346'' 349'' 2004.
33. Li X'' Zhang XL'' Shen G'' Tang GH. Effects of tensile forces on serum deprivation-induced osteoblast apoptosis: expression analysis of caspases'' Bcl-2'' and Bax. Chin Med J (Engl) 125(14):2568-2573'' 2012.
34. Li Y'' Tang L'' Duan Y'' Ding Y. Upregulation of MMP-13 and TIMP-1 expression in response to mechanical strain in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. BMC Res Notes 3:309'' 2010.
35. Liegibel UM'' Sommer U'' Tomakidi P'' Hilscher U'' Van Den Heuvel L'' Pirzer R'' Hillmeier J'' Nawroth P'' Kasperk C. Concerted action of androgens and mechanical strain shifts bone metabolism from high turnover into an osteoanabolic mode. J Exp Med 196(10):1387-1392'' 2002.
36. Lima F'' Vico L'' Lafage-Proust MH'' van der Saag P'' Alexandre C'' Thomas T. Interactions between estrogen and mechanical strain effects on U2OS human osteosarcoma cells are not influenced by estrogen receptor type. Bone 35(5):1127-1135'' 2004.
37. Liu X'' Zhang X'' Luo ZP. Strain-related collagen gene expression in human osteoblast-like cells. Cell Tissue Res 322(2):331-334'' 2005.
38. Narutomi M'' Nishiura T'' Sakai T'' Abe K'' Ishikawa H. Cyclic mechanical strain induces interleukin-6 expression via prostaglandin E2 production by cyclooxygenase-2 in MC3T3-E1 osteoblast-like cells. J Oral Biosci 49(1):65-73'' 2007.
39. Miyauchi A'' Gotoh M'' Kamioka H'' Notoya K'' Sekiya H'' Takagi Y'' Yoshimoto Y'' Ishikawa H'' Chihara K'' Takano-Yamamoto T'' Fujita T'' Mikuni-Takagaki Y. αVβ3 integrin ligands enhance volume-sensitive calcium influx in mechanically stretched osteocytes. J Bone Miner Metab 24(6):498-504'' 2006.
40. Motokawa M'' Kaku M'' Tohma Y'' Kawata T'' Fujita T'' Kohno S'' Tsutsui K'' Ohtani J'' Tenjo K'' Shigekawa M'' Kamada H'' Tanne K. Effects of cyclic tensile forces on the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and macrophage-colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) in murine osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. J Dent Res 84(5):422-427'' 2005.
41. Myers KA'' Rattner JB'' Shrive NG'' Hart DA. Osteoblast-like cells and fluid flow: cytoskeleton-dependent shear sensitivity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 364(2):214-219'' 2007. Epub 2007 Oct 4.
42. Plotkin LI'' Mathov I'' Aguirre JI'' Parfitt AM'' Manolagas SC'' Bellido T. Mechanical stimulation prevents osteocyte apoptosis: requirement of integrins'' Src kinases'' and ERKs. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 289(3):C633-643'' 2005.
43. Qi J'' Chi L'' Faber J'' Koller B'' Banes AJ. ATP reduces gel compaction in osteoblast-populated collagen gels. J Appl Physiol 102(3):1152-60'' 2007.
44. Qi J'' Chi L'' Wang J'' Sumanasinghe R'' Wall M'' Tsuzaki M'' Banes AJ. Modulation of collagen gel compaction by extracellular ATP is MAPK and NF-κB pathways dependent. Exp Cell Res 315(11):1990-2000'' 2009. Epub 2009 Feb 23.
45. Rath B'' Springorum HR'' Deschner J'' Luring C'' Tingart M'' Grifka J'' Schaumburger J'' Grassel S. Regulation of gene expression in articular cells is influenced by biomechanicalloading. Central European Journal of Medicine 2012'' doi: 10.2478/s11536-012-0008-x.
46. Robinson JA'' Chatterjee-Kishore M'' Yaworsky PJ'' Cullen DM'' Zhao W'' Li C'' Kharode Y'' Sauter L'' Babij P'' Brown EL'' Hill AA'' Akhter MP'' Johnson ML'' Recker RR'' Komm BS'' Bex FJ. Wnt/β-catenin signaling is a normal physiological response to mechanical loading in bone. J Biol Chem 281(42):31720-31728'' 2006.
47. Sano S'' Okawa A'' Nakajima A'' Tahara M'' Fujita K'' Wada Y'' Yamazaki M'' Moriya H'' Sasho T. Identification of Pip4k2β as a mechanical stimulus responsive gene and its expression during musculoskeletal tissue healing. Cell Tissue Res 323(2):245-252'' 2006.
48. Siddhivarn C'' Banes A'' Champagne C'' Riche EL'' Weerapradist W'' Offenbacher S. Prostaglandin D2 pathway and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ-1 expression are induced by mechanical loading in an osteoblastic cell line. J Periodontal Res 41(2):92-100'' 2006.
49. Siddhivarn C'' Banes A'' Champagne C'' Riche EL'' Weerapradist W'' Offenbacher S. Mechanical loading and Δ12prostaglandin J2 induce bone morphogenetic protein-2'' peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ-1'' and bone nodule formation in an osteoblastic cell line. J Periodontal Res 42(5):383-392'' 2007.
50. Stanford CM'' Stevens JW'' Brand RA. Cellular deformation reversibly depresses RT-PCR detectable levels of bone-related mRNA. Journal of Biomechanics 28(12):1419-1427'' 1995.
51. Sun Z'' Tee BC. Molecular variations related to the regional differences in periosteal growth at the mandibular ramus. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 294(1):79-87'' 2011. doi: 10.1002/ar.21293. Epub 2010 Nov 16.
52. Suzuki N'' Yoshimura Y'' Deyama Y'' Suzuki K'' Kitagawa Y. Mechanical stress directly suppresses osteoclast differentiation in RAW264.7 cells. Int J Mol Med 21(3):291-296'' 2008.
53. Tang L'' Lin Z'' Li YM. Effects of different magnitudes of mechanical strain on osteoblasts in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 344(1):122-128'' 2006. Epub 2006 Apr 17.
54. Thompson MS'' Epari DR'' Bieler F'' Duda GN. In vitro models for bone mechanobiology: applications in bone regeneration and tissue engineering. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 224(12):1533-1541'' 2010.
55. Toyoshita Y'' Iida S'' Koshino H'' Hirai T'' Yokoyama A. CYP24 promoter activity is affected by mechanical stress and mitogen-activated protein kinase in MG63 osteoblast-like cells. Nihon Hotetsu Shika Gakkai Zasshi 52(2):171-174'' 2008.
56. Vadiakas GP'' Banes AJ. Verapamil decreases cyclic load-induced calcium incorporation in ROS 17/2.8 osteosarcoma cell cultures. Matrix 12(6):439-447 '' 1992.
57. Visconti LA'' Yen EH'' Johnson RB. Effect of strain on bone nodule formation by rat osteogenic cells in vitro. Archives of Oral Biology 49(6):485-492'' 2004
58. Xiao LW'' Yang M'' Dong J'' Xie H'' Sui GL'' He YL'' Lei JX'' Liao EY'' Yuan X. Stretch-inducible expression of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) in human osteoblasts-like cells is mediated by PI3K-JNK pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 28(2):297-304'' 2011. Epub 2011 Aug 16.
59. Yamamoto N'' Fukuda K'' Matsushita T'' Matsukawa M'' Hara F'' Hamanishi C. Cyclic tensile stretch stimulates the release of reactive oxygen species from osteoblast-like cells. Calcif Tissue Int 76(6):433-8'' 2005.
60. Zhang C'' Liang G'' Zhang Y'' Hu Y. Response to dynamic strain in human periosteal cells grown in vitro. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi 23(3):546-550'' 2006.
61. Zhu J'' Zhang X'' Wang C'' Peng X'' Zhang X. Different magnitudes of tensile strain induce human osteoblasts differentiation associated with the activation of ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Int J Mol Sci 9(12):2322-2332'' 2008. Epub 2008 Nov 26.
62. Ziambaras K'' Lecanda F'' Steinberg TH'' Civitelli R. Cyclic stretch enhances gap junctional communication between osteoblastic cells. J Bone Miner Res 13(2):218-28'' 1998.
Cardiovasculature
Cardiomyocytes and fibroblasts
1. Adam RM'' Roth JA'' Cheng HL'' Rice DC'' Khoury J'' Bauer SB'' Peters CA'' Freeman MR. Signaling through PI3K/Akt mediates stretch and PDGF-BB-dependent DNA synthesis in bladder smooth muscle cells. J Urol 169(6):2388-2393'' 2003.
2. Alibin CP'' Kopilas MA'' Anderson HD. Suppression of cardiac myocyte hypertrophy by conjugated linoleic acid: role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors α and γ. J Biol Chem 283(16):10707-10715'' 2008. Epub 2008 Feb 18.
3. Anderson HD'' Wang F'' Gardner DG. Role of the epidermal growth factor receptor in signaling strain-dependent activation of the brain natriuretic peptide gene. J Biol Chem 279(10):9287-9297'' 2004.
4. Baba HA'' Stypmann J'' Grabellus F'' Kirchhof P'' Sokoll A'' Schafers M'' Takeda A'' Wilhelm MJ'' Scheld HH'' Takeda N'' Breithardt G'' Levkau B. Dynamic regulation of MEK/Erks and Akt/GSK-3β in human end-stage heart failure after left ventricular mechanical support: myocardial mechanotransduction-sensitivity as a possible molecular mechanism. Cardiovascular Research 59(2):390-399'' 2003.
5. Boateng SY'' Belin RJ'' Geenen DL'' Margulies KB'' Martin JL'' Hoshijima M'' de Tombe PP'' Russell B. Cardiac dysfunction and heart failure are associated with abnormalities in the subcellular distribution and amounts of oligomeric muscle LIM protein. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292(1):H259-H269'' 2007.
6. Boateng SY'' Lateef SS'' Mosley W'' Hartman TJ'' Hanley L'' Russell B. RGD and YIGSR synthetic peptides facilitate cellular adhesion identical to that of laminin and
fibronectin but alter the physiology of neonatal cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288(1):C30-C38'' 2005.
7. Boateng SY'' Senyo SE'' Qi L'' Goldspink PH'' Russell B. Myocyte remodeling in response to hypertrophic stimuli requires nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of muscle LIM protein. J Mol Cell Cardiol 47(4):426-35'' 2009. Epub 2009 Apr 17.
8. Boerma M'' van der Wees CG'' Vrieling H'' Svensson JP'' Wondergem J'' van der Laarse A'' Mullenders LH'' van Zeeland AA. Microarray analysis of gene expression profiles of cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts after mechanical stress'' ionising or ultraviolet radiation. BMC Genomics 6(1):6'' 2005.
9. Blaauw E'' van Nieuwenhoven FA'' Willemsen P'' Delhaas T'' Prinzen FW'' Snoeckx LH'' van Bilsen M'' van der Vusse GJ. Stretch-induced hypertrophy of isolated adult rabbit cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 299(3):H780-H787'' 2010. Epub 2010 Jul 16.
10. Cao L'' Gardner DG. Natriuretic peptides inhibit DNA synthesis in cardiac fibroblasts. Hypertension 25(2):227-234'' 1995.
11. Choudhary R'' Palm-Leis A'' Scott RC 3rd'' Guleria RS'' Rachut E'' Baker KM'' Pan J. All-trans retinoic acid prevents development of cardiac remodeling in aortic banded rats by inhibiting the renin-angiotensin system. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294(2):H633-H644'' 2008. Epub 2007 Dec 21.
12. de Jonge HW'' Dekkers DH'' Tilly BC'' Lamers JM. Cyclic stretch and endothelin-1 mediated activation of chloride channels in cultured neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. Clin Sci (Lond) 103 Suppl 48:148S-151S'' 2002.
13. Espinoza-Derout J'' Wagner M'' Shahmiri K'' Mascareno E'' Chaqour B'' Siddiqui MA. Pivotal role of cardiac lineage protein-1 (CLP-1) in transcriptional elongation factor P-TEFb complex formation in cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Res 75(1):129-138'' 2007. Epub 2007 Mar 28.
14. Földes G'' Mioulane M'' Wright JS'' Liu AQ'' Novak P'' Merkely B'' Gorelik J'' Schneider MD'' Ali NN'' Harding SE. Modulation of human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte growth: a testbed for studying human cardiac hypertrophy? J Mol Cell Cardiol 50(2):367-376'' 2011. Epub 2010 Nov 1.
15. Funari BJ'' Witt MR'' Clause KM'' Keller BB'' Tobita K'' Ralphe JC. The impact of energy substrate on contractile performance in a neonatal rat engineered cardiac tissue model [abstract]. Pediatric Academic Societies Annual Meeting'' Toronto'' Canada'' 2007.
16. Gardner DG'' Newman ED'' Nakamura KK'' Nguyen KP. Endothelin increases the synthesis and secretion of atrial natriuretic peptide in neonatal rat cardiocytes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 261:E177-E182'' 1991.
17. Gupta S'' Sen S. Myotrophin-kB DNA interaction in the initiation process of cardiac hypertrophy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)/Molecular Cell Research 1589(3):247-260'' 2002.
18. Harada M'' Saito Y'' Nakagawa O'' Miyamoto Y'' Ishikawa M'' Kuwahara K'' Ogawa E'' Nakayama M'' Kamitani S'' Hamanaka I'' Kajiyama N'' Masuda I'' Itoh H'' Tanaka I'' Nakao K. Role of cardiac nonmyocytes in cyclic mechanical stretch-induced myocyte hypertrophy. Heart Vessels Suppl 12:198-200'' 1997.
19. Heineke J'' Ruetten H'' Willenbockel C'' Gross SC'' Naguib M'' Schaefer A'' Kempf T'' Hilfiker-Kleiner D'' Caroni P'' Kraft T'' Kaiser RA'' Molkentin JD'' Drexler H'' Wollert KC. Attenuation of cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction by muscle
FLEXCELL® INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
9
LIM protein-calcineurin signaling at the sarcomeric Z-disc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(5):1655-1660'' 2005.
20. Hilfiker-Kleiner D'' Kaminski K'' Kaminska A'' Fuchs M'' Klein G'' Podewski E'' Grote K'' Kiian I'' Wollert KC'' Hilfiker A'' Drexler H. Regulation of proangiogenic factor CCN1 in cardiac muscle: impact of ischemia'' pressure overload'' and neurohumoral activation. Circulation 109(18):2227-2233'' 2004.
21. Husse B'' Sopart A'' Isenberg G. Cyclical mechanical stretch-induced apoptosis in myocytes from young rats but necrosis in myocytes from old rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285:1521-1527'' 2003.
22. Koitabashi N'' Arai M'' Kogure S'' Niwano K'' Watanabe A'' Aoki Y'' Maeno T'' Nishida T'' Kubota S'' Takigawa M'' Kurabayashi M. Increased connective tissue growth factor relative to brain natriuretic peptide as a determinant of myocardial fibrosis. Hypertension 49(5):1120-1127'' 2007. Epub 2007 Mar 19.
23. Lal H'' Verma SK'' Golden HB'' Foster DM'' Smith M'' Dostal DE. Stretch-induced regulation of angiotensinogen gene expression in cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts: opposing roles of JNK1/2 and p38α MAP kinases. J Mol Cell Cardiol 45(6):770-778'' 2008. Epub 2008 Sep 26.
24. Lal H'' Verma SK'' Smith M'' Guleria RS'' Lu G'' Foster DM'' Dostal DE. Stretch-induced MAP kinase activation in cardiac myocytes: differential regulation through β1-integrin and focal adhesion kinase. J Mol Cell Cardiol 43(2):137-147'' 2007. Epub 2007 May 24.
25. Lateef SS'' Boateng S'' Ahluwalia N'' Hartman TJ'' Russell B'' Hanley L. Three-dimensional chemical structures by protein functionalized micron-sized beads bound to polylysine-coated silicone surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res A 72(4):373-380'' 2005.
26. Lateef SS'' Boateng S'' Hartman TJ'' Crot CA'' Russell B'' Hanley L. GRGDSP peptide-bound silicone membranes withstand mechanical flexing in vitro and display enhanced fibroblast adhesion. Biomaterials 23(15):3159-3168'' 2002.
27. Liang F'' Atakilit A'' Gardner DG. Integrin dependence of brain natriuretic peptide gene promoter activation by mechanical strain. J Biol Chem 275(27):20355-20360'' 2000.
28. Liang F'' Gardner DG. Autocrine/paracrine determinants of strain-activated brain natriuretic peptide gene expression in cultured cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem 273(23):14612-14619'' 1998.
29. Liang F'' Gardner DG. Mechanical strain activates BNP gene transcription through a p38/NF-κB-dependent mechanism. J Clin Invest 104(11):1603-1612'' 1999.
30. Liang F'' Kovacic-Milivojevic B'' Chen S'' Cui J'' Roediger F'' Intengan H'' Gardner DG. Signaling mechanisms underlying strain-dependent brain natriuretic peptide gene transcription. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 79(8):640-645'' 2001.
31. Liang F'' Lu S'' Gardner DG. Endothelin-dependent and -independent components of strain-activated brain natriuretic peptide gene transcription require extracellular signal regulated kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Hypertension 35(1 Pt 2):188-192'' 2000.
32. Liang F'' Wu J'' Garami M'' Gardner DG. Mechanical strain increases expression of the brain natriuretic peptide gene in rat cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem 272(44):28050-28056'' 1997.
33. Liang YJ'' Lai LP'' Wang BW'' Juang SJ'' Chang CM'' Leu JG'' Shyu KG. Mechanical stress enhances serotonin 2B receptor modulating brain natriuretic peptide through nuclear factor-κB in cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Res 72(2):303-12'' 2006.
34. Lindahl GE'' Chambers RC'' Papakrivopoulou J'' Dawson SJ'' Jacobsen MC'' Bishop JE'' Laurent GJ. Activation of fibroblast procollagen α1(I) transcription by mechanical strain is transforming growth factor-β-dependent and involves increased binding of CCAAT-binding factor (CBF/NF-Y) at the proximal promoter. J Biol Chem 277(8):6153-6161'' 2002.
35. Malhotra R'' D’Souza KM'' Staron ML'' Birukov KG'' Bodi I'' Akhter SA. G alpha(q)-mediated activation of GRK2 by mechanical stretch in cardiac myocytes: the role of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 285(18):13748-13760'' 2010. Epub 2010 Mar 1.
36. Marin TM'' Clemente CF'' Santos AM'' Picardi PK'' Pascoal VD'' Lopes-Cendes I'' Saad MJ'' Franchini KG. Shp2 negatively regulates growth in cardiomyocytes by controlling focal adhesion kinase/Src and mTOR pathways. Circ Res 103(8):813-824'' 2008. Epub 2008 Aug 28.
37. Miller CE'' Donlon KJ'' Toia L'' Wong CL'' Chess PR. Cyclic strain induces proliferation of cultured embryonic heart cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 36(10):633-639'' 2000.
38. Nadruz W Jr'' Corat MA'' Marin TM'' Guimaraes Pereira GA'' Franchini KG. Focal adhesion kinase mediates MEF2 and c-Jun activation by stretch: role in the activation of the cardiac hypertrophic genetic program. Cardiovasc Res 68(1):87-97'' 2005.
39. Palm-Leis A'' Singh US'' Herbelin BS'' Olsovsky GD'' Baker KM'' Pan J. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatases mediate the inhibitory effects of all-trans retinoic acid on the hypertrophic growth of cardiomyocytes. J Biol Chem 279(52):54905-54917'' 2004.
40. Pan J'' Singh US'' Takahashi T'' Oka Y'' Palm-Leis A'' Herbelin BS'' Baker KM. PKC mediates cyclic stretch-induced cardiac hypertrophy through Rho family GTPases and mitogen-activated protein kinases in cardiomyocytes. J Cell Physiol 202(2):536-553'' 2005.
41. Persoon-Rothert M'' van der Wees KG'' van der Laarse A. Mechanical overload-induced apoptosis: a study in cultured neonatal ventricular myocytes and fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biochem 241(1-2):115-24'' 2002.
42. Pikkarainen S'' Tokola H'' Kerkela R'' Ilves M'' Makinen M'' Orzechowski HD'' Paul M'' Vuolteenaho O'' Ruskoaho H. Inverse regulation of preproendothelin-1 and endothelin-converting enzyme-1β genes in cardiac cells by mechanical load. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290(6):R1639-R1645'' 2006.
43. Pikkarainen S'' Tokola H'' Kerkela R'' Majalahti-Palviainen T'' Vuolteenaho O'' Ruskoaho H. Endothelin-1-specific activation of B-type natriuretic peptide gene via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear ETS factors. J Biol Chem 278(6):3969-3975'' 2003.
44. Pikkarainen S'' Tokola H'' Majalahti-Palviainen T'' Kerkela R'' Hautala N'' Bhalla SS'' Charron F'' Nemer M'' Vuolteenaho O'' Ruskoaho H. GATA-4 is a nuclear mediator of mechanical stretch-activated hypertrophic program. J Biol Chem 278(26):23807-23816'' 2003.
45. Pimentel DR'' Amin JK'' Xiao L'' Miller T'' Viereck J'' Oliver-Krasinski J'' Baliga R'' Wang J'' Siwik DA'' Singh K'' Pagano P'' Colucci WS'' Sawyer DB. Reactive oxygen
species mediate amplitude-dependent hypertrophic and apoptotic responses to mechanical stretch in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res 89(5):453-460'' 2001.
46. Prante C'' Milting H'' Kassner A'' Farr M'' Ambrosius M'' Schön S'' Seidler DG'' Banayosy AE'' Körfer R'' Kuhn J'' Kleesiek K'' Götting C. Transforming growth factor β1-regulated xylosyltransferase I activity in human cardiac fibroblasts and its impact for myocardial remodeling. J Biol Chem 282(36):26441-26449'' 2007. Epub 2007 Jul 16.
47. Rubbens MP'' Driessen-Mol A'' Boerboom RA'' Koppert MM'' van Assen HC'' TerHaar Romeny BM'' Baaijens FP'' Bouten CV. Quantification of the temporal evolution of collagen orientation in mechanically conditioned engineered cardiovascular tissues. Ann Biomed Eng 37(7):1263-1272'' 2009. Epub 2009 May 5.
48. Ruwhof C'' van Wamel AE'' Egas JM'' van der Laarse A. Cyclic stretch induces the release of growth promoting factors from cultured neonatal cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biochem 208(1-2):89-98'' 2000.
49. Ruwhof C'' van Wamel AE'' van der Valk LJ'' Schrier PI'' van der Laarse A. Direct'' autocrine and paracrine effects of cyclic stretch on growth of myocytes and fibroblasts isolated from neonatal rat ventricles. Arch Physiol Biochem 109(1):10-17'' 2001.
50. Ruwhof C'' van Wamel JT'' Noordzij LA'' Aydin S'' Harper JC'' van der Laarse A. Mechanical stress stimulates phospholipase C activity and intracellular calcium ion levels in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Cell Calcium 29(2):73-83'' 2001.
51. Senyo SE'' Koshman YE'' Russell B. Stimulus interval'' rate and direction differentially regulate phosphorylation for mechanotransduction in neonatal cardiac myocytes. FEBS Lett 581(22):4241-4247'' 2007. Epub 2007 Aug 8.
52. Shyu KG'' Ko WH'' Yang WS'' Wang BW'' Kuan P. Insulin-like growth factor-1 mediates stretch-induced upregulation of myostatin expression in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Cardiovascular Research 68(3):405-414'' 2005.
53. Sil P'' Gupta S'' Young D'' Sen S. Regulation of myotrophin gene by pressure overload and stretch. Mol Cell Biochem 262(1-2):79-89'' 2004.
54. Simmons CA'' Nikolovski J'' Thornton AJ'' Matlis S'' Mooney DJ. Mechanical stimulation and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling independently regulate osteogenic differentiation and mineralization by calcifying vascular cells. Journal of Biomechanics 37(10):1531-1541'' 2004.
55. Skurk C'' Izumiya Y'' Maatz H'' Razeghi P'' Shiojima I'' Sandri M'' Sato K'' Zeng L'' Schiekofer S'' Pimentel D'' Lecker S'' Taegtmeyer H'' Goldberg AL'' Walsh K. The FOXO3a transcription factor regulates cardiac myocyte size downstream of AKT signaling. J Biol Chem 280(21):20814-20823'' 2005.
56. Swildens J'' de Vries AA'' Li Z'' Umar S'' Atsma DE'' Schalij MJ'' van der Laarse A. Integrin stimulation favors uptake of macromolecules by cardiomyocytes in vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem 26(6):999-1010'' 2010. Epub 2011 Jan 4.
57. Tobita K'' Garrison JB'' Keller BB. Differential effects of cyclic stretch on embryonic ventricular cardiomyocyte and non-cardiomyocyte orientation. Edited by Clark EB'' Nakazawa M'' Takao A. Blackwell Futura Publishing:177-179'' 2005.
58. Tomanek RJ'' Zheng W. Role of growth factors in coronary morphogenesis. Tex Heart Inst J 29(4):250-254'' 2002.
59. Tornatore TF'' Dalla Costa AP'' Clemente CF'' Judice C'' Rocco SA'' Calegari VC'' Cardoso L'' Cardoso AC'' Gonçalves A Jr'' Franchini KG. A role for focal adhesion
kinase in cardiac mitochondrial biogenesis induced by mechanical stress. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 300(3):H902-H912'' 2011. Epub 2010 Dec 10.
60. Torsoni AS'' Constancio SS'' Nadruz W'' Jr.'' Hanks SK'' Franchini KG. Focal adhesion kinase is activated and mediates the early hypertrophic response to stretch in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res 93(2):140-147'' 2003.
61. Torsoni AS'' Marin TM'' Velloso LA'' Franchini KG. RhoA/ROCK signaling is critical to FAK activation by cyclic stretch in cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289(4):H1488-H1496'' 2005.
62. Tsai CT'' Chiang FT'' Tseng CD'' Yu CC'' Wang YC'' Lai LP'' Hwang JJ'' Lin JL. Mechanical stretch of atrial myocyte monolayer decreases sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium adenosine triphosphatase expression and increases susceptibility to repolarization alternans. J Am Coll Cardiol 58(20):2106-2115'' 2011.
63. Tulloch NL'' Muskheli V'' Razumova MV'' Korte FS'' Regnier M'' Hauch KD'' Pabon L'' Reinecke H'' Murry CE. Growth of engineered human myocardium with mechanical loading and vascular coculture. Circ Res 109(1):47-59'' 2011. Epub 2011 May 19.
64. Tyagi SC'' Lewis K'' Pikes D'' Marcello A'' Mujumdar VS'' Smiley LM'' Moore CK. Stretch-induced membrane type matrix metalloproteinase and tissue plasminogen activator in cardiac fibroblast cells. J Cell Physiol 176(2):374-382'' 1998.
65. van Kesteren CA'' Saris JJ'' Dekkers DH'' Lamers JM'' Saxena PR'' Schalekamp MA'' Danser AH. Cultured neonatal rat cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts do not synthesize renin or angiotensinogen: evidence for stretch-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy independent of angiotensin II. Cardiovascular Research 43(1):148-156'' 1999.
66. van Wamel AJ'' Ruwhof C'' van der Valk-Kokshoom LE'' Schrier PI'' van der Laarse A. The role of angiotensin II'' endothelin-1 and transforming growth factor-β as autocrine/paracrine mediators of stretch-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Mol Cell Biochem 218(1-2):113-124'' 2001.
67. van Wamel AJ'' Ruwhof C'' van der Valk-Kokshoorn LJ'' Schrier PI'' van der Laarse A. Stretch-induced paracrine hypertrophic stimuli increase TGF-β1 expression in cardiomyocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 236(1-2):147-153'' 2002.
68. van Wamel JE'' Ruwhof C'' van der Valk-Kokshoorn EJ'' Schrier PI'' van der Laarse A. Rapid gene transcription induced by stretch in cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts and their paracrine influence on stationary myocytes and fibroblasts. Pflugers Arch 439(6):781-788'' 2000.
69. Wang BW'' Hung HF'' Chang H'' Kuan P'' Shyu KG. Mechanical stretch enhances the expression of resistin gene in cultured cardiomyocytes via tumor necrosis factor-α. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293(4):H2305-H2312'' 2007. Epub 2007 Jun 15.
70. Watson CJ'' Phelan D'' Xu M'' Collier P'' Neary R'' Smolenski A'' Ledwidge M'' McDonald K'' Baugh J. Mechanical stretch up-regulates the B-type natriuretic peptide system in human cardiac fibroblasts: a possible defense against transforming growth factor-β mediated fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 5(1):9'' 2012.
71. Wei CC'' Chen Y'' Powell LC'' Zheng J'' Shi K'' Bradley WE'' Powell PC'' Ahmad S'' Ferrario CM'' Dell’Italia LJ. Cardiac kallikrein-kinin system is upregulated in chronic volume overload and mediates an inflammatory induced collagen loss. PLoS One 7(6):e40110'' 2012. Epub 2012 Jun 29.
72. Xi YT'' Bai XJ'' Wu GR'' Ma AQ. Centrifugal force stretcher a new of in vitro mechanical cell stimulator. Sheng Li Xue Bao 56(3):419-423'' 2004.
73. Yokoyama T'' Sekiguchi K'' Tanaka T'' Tomaru K'' Arai M'' Suzuki T'' Nagai R. Angiotensin II and mechanical stretch induce production of tumor necrosis factor in cardiac fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 276:H1968-H1976'' 1999.
74. Zheng W'' Seftor EA'' Meininger CJ'' Hendrix MJ'' Tomanek RJ. Mechanisms of coronary angiogenesis in response to stretch: role of VEGF and TGF-β. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280(2):H909-H917'' 2001.
75. Zhou C'' Ziegler C'' Birder LA'' Stewart AF'' Levitan ES. Angiotensin II and stretch activate NADPH oxidase to destabilize cardiac Kv4.3 channel mRNA. Circ Res 98(8):1040-1047'' 2006.
Cardiovascular endothelial cells
76. Ali MH'' Pearlstein DP'' Mathieu CE'' Schumacker PT. Mitochondrial requirement for endothelial responses to cyclic strain: implications for mechanotransduction. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 287(3):L486-L496'' 2004.
77. Awolesi MA'' Sessa WC'' Sumpio BE. Cyclic strain upregulates nitric oxide synthase in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. J Clin Invest 96(3):1449-1454'' 1995.
78. Azuma N'' Duzgun SA'' Ikeda M'' Kito H'' Akasaka N'' Sasajima T'' Sumpio BE. Endothelial cell response to different mechanical forces. J Vasc Surg 32(4):789-794'' 2000.
79. Baker PN'' Stranko CP'' Davidge ST'' Davies PS'' Roberts JM. Mechanical stress eliminates the effects of plasma from patients with preeclampsia on endothelial cells. Am J Obstet Gynecol 174(2):730-6'' 1996.
80. Brophy CM'' Mills I'' Rosales O'' Isales C'' Sumpio BE. Phospholipase C: a putative mechanotransducer for endothelial cell response to acute hemodynamic changes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 190(2):576-581'' 1993.
81. Cevallos M'' Riha GM'' Wang X'' Yang H'' Yan S'' Li M'' Chai H'' Yao Q'' Chen C. Cyclic strain induces expression of specific smooth muscle cell markers in human endothelial cells. Differentiation 74(9-10):552-561'' 2006.
82. Chang H'' Wang BW'' Kuan P'' Shyu KG. Cyclical mechanical stretch enhances angiopoietin-2 and Tie2 receptor expression in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Clin Sci (Lond) 104(4):421-428'' 2003.
83. Cheng JJ'' Chao YJ'' Wang DL. Cyclic strain activates redox-sensitive proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (PYK2) in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 277(50):48152-48157'' 2002.
84. Cheng JJ'' Wung BS'' Chao YJ'' Wang DL. Cyclic strain enhances adhesion of monocytes to endothelial cells by increasing intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression. Hypertension 28(3):386-391'' 1996.
85. Cheng JJ'' Wung BS'' Chao YJ'' Wang DL. Cyclic strain-induced reactive oxygen species involved in ICAM-1 gene induction in endothelial cells. Hypertension 31(1):125-30'' 1998.
86. Cheng JJ'' Wung BS'' Chao YJ'' Wang DL. Sequential activation of protein kinase C (PKC)-α and PKC-ε contributes to sustained Raf/ERK1/2 activation in endothelial cells under mechanical strain. J Biol Chem 276(33):31368-31375'' 2001.
FLEXCELL® INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
14
87. Coen P'' Cummins P'' Birney Y'' Devery R'' Cahill P. Modulation of nitric oxide and 6-keto-prostaglandin F(1α) production in bovine aortic endothelial cells by conjugated linoleic acid. Endothelium 11(3-4):211-20'' 2004.
88. Cohen CR'' Mills I'' Du W'' Kamal K'' Sumpio BE. Activation of the adenylyl cyclase/cyclic AMP/protein kinase A pathway in endothelial cells exposed to cyclic strain. Exp Cell Res 231(1):184-189'' 1997.
89. Cummins PM'' Cotter EJ'' Cahill PA. Hemodynamic regulation of metallopeptidases within the vasculature. Protein Pept Lett 11(5):433-442'' 2004.
90. Cummins PM'' von Offenberg Sweeney N'' Killeen MT'' Birney YA'' Redmond EM'' Cahill PA. Cyclic strain-mediated matrix metalloproteinase regulation within the vascular endothelium: a force to be reckoned with. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292:H28–H42'' 2007.
91. Dekker RJ'' van Thienen JV'' Rohlena J'' de Jager SC'' Elderkamp YW'' Seppen J'' de Vries CJ'' Biessen EA'' van Berkel TJ'' Pannekoek H'' Horrevoets AJ. Endothelial KLF2 links local arterial shear stress levels to the expression of vascular tone-regulating genes. Am J Pathol 167(2):609-618'' 2005.
92. Du W'' Mills I'' Sumpio BE. Cyclic strain causes heterogeneous induction of transcription factors'' AP-1'' CRE binding protein and NF-kB'' in endothelial cells: species and vascular bed diversity. Journal of Biomechanics 28(12):1485-149'' 1995.
93. Evans L'' Frenkel L'' Brophy CM'' Rosales O'' Sudhaker CB'' Li G'' Du W'' Sumpio BE. Activation of diacylglycerol in cultured endothelial cells exposed to cyclic strain. Am J Physiol 272(2 Pt 1):C650-C656'' 1997.
94. Fisslthaler B'' Boengler K'' Fleming I'' Schaper W'' Busse R'' Deindl E. Identification of a cis-element regulating transcriptional activity in response to fluid shear stress in bovine aortic endothelial cells. Endothelium 10(4-5):267-75'' 2003.
95. Fisslthaler B'' Popp R'' Michaelis UR'' Kiss L'' Fleming I'' Busse R. Cyclic stretch enhances the expression and activity of coronary endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor synthase. Hypertension 38(6):1427-1432'' 2001.
96. Fujioka K'' Azuma N'' Kito H'' Gahtan V'' Esato K'' Sumpio BE. Role of caveolin in hemodynamic force-mediated endothelial changes. J Surg Res 92(1):7-10'' 2000.
97. Ghosh K'' Thodeti CK'' Dudley AC'' Mammoto A'' Klagsbrun M'' Ingber DE. Tumor-derived endothelial cells exhibit aberrant Rho-mediated mechanosensing and abnormal angiogenesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(32):11305-11310'' 2008. Epub 2008 Aug 6.
98. Goettsch C'' Goettsch W'' Arsov A'' Hofbauer LC'' Bornstein SR'' Morawietz H. Long-term cyclic strain downregulates endothelial Nox4. Antioxid Redox Signal 11(10):2385-2397'' 2009.
99. Grigoryev DN'' Ma SF'' Irizarry RA'' Ye SQ'' Quackenbush J'' Garcia JG. Orthologous gene-expression profiling in multi-species models: search for candidate genes. Genome Biol 5(5):R34'' 2004. Epub 2004 Apr 27.
100. Haga M'' Chen A'' Gortler D'' Dardik A'' Sumpio BE. Shear stress and cyclic strain may suppress apoptosis in endothelial cells by different pathways. Endothelium 10(3):149-57'' 2003.
101. Hishikawa K'' Luscher TF. Pulsatile stretch stimulates superoxide production in human aortic endothelial cells. Circulation 96(10):3610-3616'' 1997.
FLEXCELL® INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
15
102. Hoshino Y'' Nishimura K'' Sumpio BE. Phosphatase PTEN is inactivated in bovine aortic endothelial cells exposed to cyclic strain. J Cell Biochem 100(2):515-526'' 2007.
103. Howard AB'' Alexander RW'' Nerem RM'' Griendling KK'' Taylor WR. Cyclic strain induces an oxidative stress in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 272(2):C421-C427'' 1997.
104. Iba T'' Mills I'' Sumpio BE. Intracellular cyclic AMP levels in endothelial cells subjected to cyclic strain in vitro. J Surg Res 52(6):625-630'' 1992.
105. Iba T'' Shin T'' Sonoda T'' Rosales O'' Sumpio BE. Stimulation of endothelial secretion of tissue-type plasminogen activator by repetitive stretch. J Surg Res 50(5):457-460'' 1991.
106. Iba T'' Sumpio BE. Morphological response of human endothelial cells subjected to cyclic strain in vitro. Microvasc Res 42(3):245-254'' 1991.
107. Ikeda M'' Kito H'' Sumpio BE. Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase dependent MAP kinase activation via p21ras in endothelial cells exposed to cyclic strain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 257(3):668-671'' 1999.
108. Ikeda M'' Takei T'' Mills I'' Kito H'' Sumpio BE. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 activation in endothelial cells exposed to cyclic strain. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 276:H614-H622'' 1999.
109. Ikeda M'' Takei T'' Mills I'' Sumpio BE. Calcium-independent activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 by cyclic strain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 247(2):462-465'' 1998.
110. Juan SH'' Chen JJ'' Chen CH'' Lin H'' Cheng CF'' Liu JC'' Hsieh MH'' Chen YL'' Chao HH'' Chen TH'' Chan P'' Cheng TH. 17β-estradiol inhibits cyclic strain-induced endothelin-1 gene expression within vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287(3):H1254-H1261'' 2004.
111. Kim JI'' Cordova AC'' Hirayama Y'' Madri JA'' Sumpio BE. Differential effects of shear stress and cyclic strain on Sp1 phosphorylation by protein kinase Czeta modulates membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase in endothelial cells. Endothelium 15(1):33-42'' 2008.
112. Kito H'' Yokoyama C'' Inoue H'' Tanabe T'' Nakajima N'' Sumpio BE. Cyclooxygenase expression in bovine aortic endothelial cells exposed to cyclic strain. Endothelium 6(2):107-112'' 1998.
113. Korff T'' Aufgebauer K'' Hecker M. Cyclic stretch controls the expression of CD40 in endothelial cells by changing their transforming growth factor-β1 response. Circulation 116(20):2288-2297'' 2007. Epub 2007 Oct 29.
114. Kou B'' Zhang J'' Singer DR. Effects of cyclic strain on endothelial cell apoptosis and tubulogenesis are dependent on ROS production via NAD(P)H subunit p22phox. Microvasc Res 77(2):125-133'' 2009. Epub 2008 Aug 27.
115. Lauth M'' Cattaruzza M'' Hecker M. ACE inhibitor and AT1 antagonist blockade of deformation-induced gene expression in the rabbit jugular vein through B2 receptor activation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21(1):61-6'' 2001.
116. Lauth M'' Wagner AH'' Cattaruzza M'' Orzechowski HD'' Paul M'' Hecker M. Transcriptional control of deformation-induced preproendothelin-1 gene expression in endothelial cells. J Mol Med 78(8):441-450'' 2000.
FLEXCELL® INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
16
117. Lee T'' Kim SJ'' Sumpio BE. Role of PP2A in the regulation of p38 MAPK activation in bovine aortic endothelial cells exposed to cyclic strain. J Cell Physiol 194(3):349-355'' 2003.
118. Li W'' Sumpio BE. Strain-induced vascular endothelial cell proliferation requires PI3K-dependent mTOR-4E-BP1 signal pathway. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288(4):H1591-1597'' 2005.
119. Metzler SA'' Pregonero CA'' Butcher JT'' Burgess SC'' Warnock JN. Cyclic strain regulates pro-inflammatory protein expression in porcine aortic valve endothelial cells. J Heart Valve Dis 17(5):571-577'' 2008.
120. Moldobaeva A'' Jenkins J'' Wagner E. Effects of distension on airway inflammation and venular P-selectin expression. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 295(5):L941-L948'' 2008. Epub 2008 Sep 19.
121. Morrow D'' Cullen JP'' Cahill PA'' Redmond EM. Cyclic strain regulates the Notch/CBF-1 signaling pathway in endothelial cells: role in angiogenic activity. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:1289-1296'' 2007.
122. Murata K'' Mills I'' Sumpio BE. Protein phosphatase 2A in stretch-induced endothelial cell proliferation. J Cell Biochem 63(3):311-319'' 1996.
123. Nishimura K'' Li W'' Hoshino Y'' Kadohama T'' Asada H'' Ohgi S'' Sumpio BE. Role of AKT in cyclic strain-induced endothelial cell proliferation and survival. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 290(3):C812-C821'' 2006.
124. Okada M'' Matsumori A'' Ono K'' Furukawa Y'' Shioi T'' Iwasaki A'' Matsushima K'' Sasayama S. Cyclic stretch upregulates production of interleukin-8 and monocyte chemotactic and activating factor/monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in human endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18(6):894-901'' 1998.
125. Pikkarainen S'' Tokola H'' Kerkela R'' Ilves M'' Makinen M'' Orzechowski HD'' Paul M'' Vuolteenaho O'' Ruskoaho H. Inverse regulation of preproendothelin-1 and endothelin-converting enzyme-1β genes in cardiac cells by mechanical load. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290(6):R1639-R1645'' 2006.
126. Rakugi H'' Yu H'' Kamitani A'' Nakamura Y'' Ohishi M'' Kamide K'' Nakata Y'' Takami S'' Higaki J'' Ogihara T. Links between hypertension and myocardial infarction. American Heart Journal 132(1 Pt 2 Su):213-221'' 1996.
127. Regnault V'' Perret-Guillaume C'' Kearney-Schwartz A'' Max JP'' Labat C'' Louis H'' Wahl D'' Pannier B'' Lecompte T'' Weryha G'' Challande P'' Safar ME'' Benetos A'' Lacolley P. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor: a new link among arterial stiffness'' pulse pressure'' and coagulation in postmenopausal women. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31(5):1226-1232'' 2011. Epub 2011 Feb 3.
128. Rosales OR'' Isales CM'' Barrett PQ'' Brophy C'' Sumpio BE. Exposure of endothelial cells to cyclic strain induces elevations of cytosolic Ca2+ concentration through mobilization of intracellular and extracellular pools. Biochem J 326(Pt 2):385-92'' 1997.
129. Rosales OR'' Sumpio BE. Changes in cyclic strain increase inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 262(4):C956-C962'' 1992.
130. Schneider SW'' Yano Y'' Sumpio BE'' Jena BP'' Geibel JP'' Gekle M'' Oberleithner H. Rapid aldosterone-induced cell volume increase of endothelial cells measured by the atomic force microscope. Cell Biol Int 21(11):759-768'' 1997.
FLEXCELL® INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
17
131. Segurola RJ Jr'' Oluwole B'' Mills I'' Yokoyama C'' Tanabe T'' Kito H'' Nakajima N'' Sumpio BE. Cyclic strain is a weak inducer of prostacyclin synthase expression in bovine aortic endothelial cells. J Surg Res 69(1):135-138'' 1997.
132. Sumpio BE'' Banes AJ'' Buckley M'' Johnson G Jr. Alterations in aortic endothelial cell morphology and cytoskeletal protein synthesis during cyclic tensional deformation. J Vasc Surg 7(1):130-138'' 1988.
133. Sumpio BE'' Banes AJ'' Levin LG'' Johnson G Jr. Mechanical stress stimulates aortic endothelial cells to proliferate. J Vasc Surg 6(3):252-256'' 1987.
134. Sumpio BE'' Banes AJ'' Link GW'' Iba T. Modulation of endothelial cell phenotype by cyclic stretch: inhibition of collagen production. J Surg Res 48(5):415-420'' 1990.
135. Sumpio BE'' Banes AJ. Prostacyclin synthetic activity in cultured aortic endothelial cells undergoing cyclic mechanical deformation. Surgery 104(2):383-389'' 1988.
136. Sumpio BE'' Chang R'' Xu WJ'' Wang XJ'' Du W. Regulation of tPA in endothelial cells exposed to cyclic strain: role of CRE'' AP-2'' and SSRE binding sites. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 273:C1441-C1448'' 1997.
137. Sumpio BE'' Du W'' Galagher G'' Wang X'' Khachigian LM'' Collins T'' Gimbrone MA Jr'' Resnick N. Regulation of PDGF-B in endothelial cells exposed to cyclic strain. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18(3):349-355'' 1998.
138. Thodeti CK'' Matthews B'' Ravi A'' Mammoto A'' Ghosh K'' Bracha AL'' Ingber DE. TRPV4 channels mediate cyclic strain-induced endothelial cell reorientation through integrin-to-integrin signaling. Circ Res 104(9):1123-1130'' 2009. Epub 2009 Apr 9.
139. Tomanek RJ'' Zheng W. Role of growth factors in coronary morphogenesis. Tex Heart Inst J 29(4):250-254'' 2002.
140. Ulfhammer E'' Ridderstrale W'' Andersson M'' Karlsson L'' Hrafnkelsdottir T'' Jern S. Prolonged cyclic strain impairs the fibrinolytic system in cultured vascular endothelial cells. J Hypertens 23(8):1551-1557'' 2005.
141. Upchurch GR Jr'' Loscalzo J'' Banes AJ. Changes in the amplitude of cyclic load biphasically modulate endothelial cell DNA synthesis and division. Vasc Med 2(1):19-24'' 1997.
142. van Wamel AJ'' Ruwhof C'' van der Valk-Kokshoom LE'' Schrier PI'' van der Laarse A. The role of angiotensin II'' endothelin-1 and transforming growth factor-β as autocrine/paracrine mediators of stretch-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Mol Cell Biochem 218(1-2):113-124'' 2001.
143. van Wamel AJ'' Ruwhof C'' van der Valk-Kokshoorn LJ'' Schrier PI'' van der Laarse A. Stretch-induced paracrine hypertrophic stimuli increase TGF-β1 expression in cardiomyocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 236(1-2):147-153'' 2002.
144. Vollmer T'' Hinse D'' Kleesiek K'' Dreier J. Interactions between endocarditis-derived Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. Gallolyticus isolates and human endothelial cells. BMC Microbiology 10:78'' 2010.
145. von Offenberg Sweeney N'' Cummins PM'' Birney YA'' Cullen JP'' Redmond EM'' Cahill PA. Cyclic strain-mediated regulation of endothelial matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression and activity. Cardiovascular Research 63(4):625-634'' 2004.
146. von Offenberg Sweeney N'' Cummins PM'' Birney YA'' Redmond EM'' Cahill PA. Cyclic strain-induced endothelial MMP-2: role in vascular smooth muscle cell migration. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 320:325–333'' 2004.
FLEXCELL® INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
18
147. von Offenberg Sweeney'' Cummins PM'' Cotter EJ'' Fitzpatrick PA'' Birney YA'' Redmond EM'' Cahill PA. Cyclic strain-mediated regulation of vascular endothelial cell migration and tube formation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 329:573–582'' 2005.
148. Wang C'' Jiao C'' Hanlon HD'' Zheng W'' Tomanek RJ'' Schatteman GC. Mechanical'' cellular'' and molecular factors interact to modulate circulating endothelial cell progenitors. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286(5):H1985-H1993'' 2004. Epub 2004 Jan 8.
149. Wang DL'' Wung BS'' Peng YC'' Wang JJ. Mechanical strain increases endothelin-1 gene expression via protein kinase C pathway in human endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 163(2):400-406'' 1995.
150. Wang DL'' Wung BS'' Shyy YJ'' Lin CF'' Chao YJ'' Usami S'' Chien S. Mechanical strain induces monocyte chemotactic protein-1 gene expression in endothelial cells. Effects of mechanical strain on monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells. Circ Res 77(2):294-302'' 1995.
151. Widmann MD'' Letsou GV'' Phan S'' Baldwin JC'' Sumpio BE. Isolation and characterization of rabbit cardiac endothelial cells: Response to cyclic strain and growth factors in vitro. Journal of Surgical Research 53(4):331-334'' 1992.
152. Wilson CJ'' Kasper G'' Schütz MA'' Duda GN. Cyclic strain disrupts endothelial network formation on Matrigel. Microvasc Res 78(3):358-63'' 2009. Epub 2009 Aug 18.
153. Woodell JE'' LaBerge M'' Langan EM 3rd'' Hilderman RH. In vitro strain-induced endothelial cell dysfunction determined by DNA synthesis. Proc Inst Mech Eng [H] 217(1):13-20'' 2003.
154. Woodell JE'' LaBerge M'' Langan EM 3rd'' Hilderman RH. P1''P4-diadenosine 5’-tetraphosphate induced DNA synthesis in mechanically injured cultured endothelial cells. Proc Inst Mech Eng [H] 217(1):21-26'' 2003.
155. Wung BS'' Cheng JJ'' Chao YJ'' Hsieh HJ'' Wang DL. Modulation of Ras/Raf/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway by reactive oxygen species is involved in cyclic strain-induced early growth response-1 gene expression in endothelial cells. Circ Res 84(7):804-812'' 1999.
156. Wung BS'' Cheng JJ'' Chao YJ'' Lin J'' Shyy YJ'' Wang DL. Cyclical strain increases monocyte chemotactic protein-1 secretion in human endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 270(4):H1462-H1468'' 1996.
157. Wung BS'' Cheng JJ'' Hsieh HJ'' Shyy YJ'' Wang DL. Cyclic strain-induced monocyte chemotactic protein-1 gene expression in endothelial cells involves reactive oxygen species activation of activator protein 1. Circ Res 81(1):1-7'' 1997.
158. Wung BS'' Cheng JJ'' Shyue SK'' Wang DL. NO modulates monocyte chemotactic protein-1 expression in endothelial cells under cyclic strain. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21(12):1941-1947'' 2001.
159. Yamaguchi S'' Yamaguchi M'' Yatsuyanagi E'' Yun SS'' Nakajima N'' Madri JA'' Sumpio BE. Cyclic strain stimulates early growth response gene product 1-mediated expression of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase in endothelium. Lab Invest 82(7):949-956'' 2002.
160. Yano Y'' Geibel J'' Sumpio BE. Cyclic strain induces reorganization of integrin α5β1 and α2β1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Cell Biochem 64(3):505-513'' 1997.
FLEXCELL® INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
19
161. Yano Y'' Geibel J'' Sumpio BE. Tyrosine phosphorylation of pp125FAK and paxillin in aortic endothelial cells induced by mechanical strain. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 271:C635-C649'' 1996.
162. Yano Y'' Saito Y'' Narumiya S'' Sumpio BE. Involvement of rho p21 in cyclic strain-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (pp125FAK)'' morphological changes and migration of endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 224(2):508-515'' 1996.
163. Zheng W'' Christensen LP'' Tomanek RJ. Stretch induces upregulation of key tyrosine kinase receptors in microvascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287(6):H2739-H2745'' 2004.
164. Zheng W'' Seftor EA'' Meininger CJ'' Hendrix MJ'' Tomanek RJ. Mechanisms of coronary angiogenesis in response to stretch: role of VEGF and TGF-β. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280(2):H909-H917'' 2001.
165. Zheng W'' Christensen LP'' Tomanek RJ. Differential effects of cyclic and static stretch on coronary microvascular endothelial cell receptors and vasculogenic/angiogenic responses. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H794–H800'' 2008.
Cardiovascular smooth muscle cells
166. Allison DA'' Wight TN'' Ripp NJ'' Braun KR'' Grande-Allen KJ. Endogenous overexpression of hyaluronan synthases within dynamically cultured collagen gels: Implications for vascular and valvular disease. Biomaterials 29:2969-2976'' 2008.
167. Birukov KG'' Shirinsky VP'' Stepanova OV'' Tkachuk VA'' Hahn AW'' Resink TJ'' Smirnov VN. Stretch affects phenotype and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Cell Biochem 144(2):131-139'' 1995.
168. Capers Q 4th'' Alexander RW'' Lou P'' De Leon H'' Wilcox JN'' Ishizaka N'' Howard AB'' Taylor WR. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in aortic tissues of hypertensive rats. Hypertension 30(6):1397-1402'' 1997.
169. Cattaruzza M'' Berger MM'' Ochs M'' Fayyazi A'' Fuzesi L'' Richter J'' Hecker M. Deformation-induced endothelin B receptor-mediated smooth muscle cell apoptosis is matrix-dependent. Cell Death Differ 9(2):219-226'' 2002.
170. Cattaruzza M'' Dimigen C'' Ehrenreich H'' Hecker M. Stretch-induced endothelin B receptor-mediated apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. FASEB J 14(7):991-998'' 2000.
171. Chang H'' Shyu KG'' Wang BW'' Kuan P. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α by cyclical mechanical stretch in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Clin Sci (Lond) 105(4):447-456'' 2003.
172. Chapman GB'' Durante W'' Hellums JD'' Schafer AI. Physiological cyclic stretch causes cell cycle arrest in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 278:H748-H754'' 2000.
173. Chen AH'' Gortler DS'' Kilaru S'' Araim O'' Frangos SG'' Sumpio BE. Cyclic strain activates the pro-survival Akt protein kinase in bovine aortic smooth muscle cells. Surgery 130(2):378-381'' 2001.
174. Chen Q'' Li W'' Quan Z'' Sumpio BE. Modulation of vascular smooth muscle cell alignment by cyclic strain is dependent on reactive oxygen species and P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Vasc Surg 37(3):660-668'' 2003.
FLEXCELL® INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
20
175. Cheng J'' Du J. Mechanical stretch simulates proliferation of venous smooth muscle cells through activation of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27(8):1744-1751'' 2007. Epub 2007 May 31.
176. Cheng J'' Zhang J'' Merched A'' Zhang L'' Zhang P'' Truong L'' Boriek AM'' Du J. Mechanical stretch inhibits oxidized low density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells by up-regulating integrin αVβ3 and stablization of PINCH-1. J Biol Chem 282(47):34268-34275'' 2007. Epub 2007 Sep 18.
177. Cheng WP'' Hung HF'' Wang BW'' Shyu KG. The molecular regulation of GADD153 in apoptosis of cultured vascular smooth muscle cells by cyclic mechanical stretch. Cardiovascular Research 77:551–559'' 2008.
178. Clements ML'' Banes AJ'' Faber JE. Effect of mechanical loading on vascular α1D- and α1B-adrenergic receptor expression. Hypertension 29(5):1156-1164'' 1997.
179. Clements ML'' Faber JE. Mechanical load opposes angiotensin-mediated decrease in vascular α1-adrenoceptors. Hypertension 29(5):1165-1172'' 1997.
180. Colombo A'' Guha S'' Mackle JN'' Cahill PA'' Lally C. Cyclic strain amplitude dictates the growth response of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro: role in in-stent restenosis and inhibition with a sirolimus drug-eluting stent'' 2012 Sep 8. [Epub ahead of print]
181. Cunningham JJ'' Linderman JJ'' Mooney DJ. Externally applied cyclic strain regulates localization of focal contact components in cultured smooth muscle cells. Ann Biomed Eng 30(7):927-935'' 2002.
182. Dangers M'' Kiyan J'' Grote K'' Schieffer B'' Haller H'' Dumler I. Mechanical stress modulates SOCS-1 expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells. J Vasc Res 47(5):432-440'' 2010. Epub 2010 Feb 6.
183. Davis MG'' Ali S'' Leikauf GD'' Dorn GW 2nd. Tyrosine kinase inhibition prevents deformation-stimulated vascular smooth muscle growth. Hypertension 24(6):706-713'' 1994.
184. Dethlefsen SM'' Shepro D'' D’Amore PA. Comparison of the effects of mechanical stimulation on venous and arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro. J Vasc Res 33(5):405-413'' 1996.
185. de Waard V'' Arkenbout EK'' Vos M'' Mocking AI'' Niessen HW'' Stooker W'' de Mol BA'' Quax PH'' Bakker EN'' VanBavel E'' Pannekoek H'' de Vries CJ. TR3 nuclear orphan receptor prevents cyclic stretch-induced proliferation of venous smooth muscle cells. Am J Pathol 168:2027–2035'' 2006.
186. Faber JE'' Yang N'' Xin X. Expression of α-adrenoceptor subtypes by smooth muscle cells and adventitial fibroblasts in rat aorta and in cell culture. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298(2):441-452'' 2001.
187. Grote K'' Bavendiek U'' Grothusen C'' Flach I'' Hilfiker-Kleiner D'' Drexler H'' Schieffer B. Stretch-inducible expression of the angiogenic factor CCN1 in vascular smooth muscle cells is mediated by Egr-1. J Biol Chem 279(53):55675-55681'' 2004.
188. Grote K'' Flach I'' Luchtefeld M'' Akin E'' Holland SM'' Drexler H'' Schieffer B. Mechanical stretch enhances mRNA expression and proenzyme release of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) via NAD(P)H oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species. Circ Res 92(11):e80-86'' 2003.
189. Hamada K'' Takuwa N'' Yokoyama K'' Takuwa Y. Stretch activates Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase in vascular smooth muscle cells through
FLEXCELL® INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
21
mechanisms involving autocrine ATP stimulation of purinoceptors. J Biol Chem 273(11):6334-6340'' 1998.
190. Han O'' Takei T'' Basson M'' Sumpio BE. Translocation of PKC isoforms in bovine aortic smooth muscle cells exposed to strain. J Cell Biochem 80(3):367-372'' 2001.
191. Hipper A'' Isenberg G. Cyclic mechanical strain decreases the DNA synthesis of vascular smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch 440(1):19-27'' 2000.
192. Hishikawa K'' Oemar BS'' Yang Z'' Luscher TF. Pulsatile stretch stimulates superoxide production and activates nuclear factor-κB in human coronary smooth muscle. Circ Res 81(5):797-803'' 1997.
193. Hitomi H'' Fukui T'' Moriwaki K'' Matsubara K'' Sun GP'' Rahman M'' Nishiyama A'' Kiyomoto H'' Kimura S'' Ohmori K'' Abe Y'' Kohno M. Synergistic effect of mechanical stretch and angiotensin II on superoxide production via NADPH oxidase in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Hypertens 24(6):1097-1104'' 2006.
194. Hoffmann SE'' Kuriakose M'' Songu-Mize E. Stretch-induced downregulation of TRPC4 does not decrease capacitative calcium entry in vascular smooth muscle cells [abstract]. Hypertension 46:P80'' 2005.
195. Hoffmann SE'' Kuriakose M'' Songu-Mize E. Stretch-induced TRPC4 downregulation in RASM cells may be due to changes in intracellular calcium [abstract]. FASEB J 20:699.17'' 2006.
196. Howard AB'' Alexander RW'' Nerem RM'' Griendling KK'' Taylor WR. Cyclic strain induces an oxidative stress in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 272(2):C421-C427'' 1997.
197. Hu Y'' Bock G'' Wick G'' Xu Q. Activation of PDGF receptor α in vascular smooth muscle cells by mechanical stress. FASEB J 12(12):1135-1142'' 1998.
198. Iwasaki H'' Eguchi S'' Ueno H'' Marumo F'' Hirata Y. Mechanical stretch stimulates growth of vascular smooth muscle cells via epidermal growth factor receptor. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 278(2):H521-H529'' 2000.
199. Iwasaki H'' Yoshimoto T'' Sugiyama T'' Hirata Y. Activation of cell adhesion kinase ß by mechanical stretch in vascular smooth muscle cells. Endocrinology 144(6):2304-2310'' 2003.
200. Jiang MJ'' Yu YJ'' Chen YL'' Lee YM'' Hung LS. Cyclic strain stimulates monocyte chemotactic protein-1 mRNA expression in smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biochem 76(2):303-310'' 2000.
201. Kakisis JD'' Pradhan S'' Cordova A'' Liapis CD'' Sumpio BE. The role of STAT-3 in the mediation of smooth muscle cell response to cyclic strain. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37(7):1396-1406'' 2005.
202. Kawabe J'' Okumura S'' Lee MC'' Sadoshima J'' Ishikawa Y. Translocation of caveolin regulates stretch-induced ERK activity in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286(5):H1845-1852'' 2004.
203. Kim BS'' Nikolovski J'' Bonadio J'' Mooney DJ. Cyclic mechanical strain regulates the development of engineered smooth muscle tissue. Nat Biotech 17(10):979-983'' 1999.
204. Kogata N'' Tribe RM'' Fässler R'' Way M'' Adams RH. Integrin-linked kinase controls vascular wall formation by negatively regulating Rho/ROCK-mediated vascular smooth muscle cell contraction. Genes Dev 23(19):2278-2283'' 2009.
FLEXCELL® INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
22
205. Kona S'' Chellamuthu P'' Xu H'' Hills SR'' Nguyen KT. Effects of cyclic strain and growth factors on vascular smooth muscle cell responses. Open Biomed Eng J 3:28-38'' 2009.
206. Kozai T'' Eto M'' Yang Z'' Shimokawa H'' Luscher TF. Statins prevent pulsatile stretch-induced proliferation of human saphenous vein smooth muscle cells via inhibition of Rho/Rho-kinase pathway. Cardiovasc Res 68(3):475-482'' 2005.
207. Kurpinski K'' Park J'' Thakar RG'' Li S. Regulation of vascular smooth muscle cells and mesenchymal stem cells by mechanical strain. Mol Cell Biomech 3(1):21-34'' 2006.
208. Li C'' Hu Y'' Mayr M'' Xu Q. Cyclic strain stress-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphatase 1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells is regulated by Ras/Rac-MAPK pathways. J Biol Chem 274(36):25273-25280'' 1999.
209. Li C'' Hu Y'' Sturm G'' Wick G'' Xu Q. Ras/Rac-Dependent activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases in smooth muscle cells stimulated by cyclic strain stress. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20(3):E1-E9'' 2000.
210. Li Q'' Muragaki Y'' Hatamura I'' Ueno H'' Ooshima A. Stretch-induced collagen synthesis in cultured smooth muscle cells from rabbit aortic media and a possible involvement of angiotensin II and transforming growth factor-β. J Vasc Res 35(2):93-103'' 1998.
211. Li W'' Chen Q'' Mills I'' Sumpio BE. Involvement of S6 kinase and p38 mitogen activated protein kinase pathways in strain-induced alignment and proliferation of bovine aortic smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol 195(2):202-209'' 2003.
212. Licht AH'' Nübel T'' Feldner A'' Jurisch-Yaksi N'' Marcello M'' Demicheva E'' Hu JH'' Hartenstein B'' Augustin HG'' Hecker M'' Angel P'' Korff T'' Schorpp-Kistner M. Junb regulates arterial contraction capacity'' cellular contractility'' and motility via its target Myl9 in mice. J Clin Invest 120(7):2307-2318'' 2010. doi: 10.1172/JCI41749. Epub 2010 Jun 14.
213. Lindsey-Hoffmann SE'' Songu-Mize E. Cyclic stretch decreases capacitative calcium entry in vascular smooth muscle cells from resistance and conduit vessels [abstract]. Experimental Biology'' 2007.
214. Ling S'' Deng G'' Ives HE'' Chatterjee K'' Rubanyi GM'' Komesaroff PA'' Sudhir K. Estrogen inhibits mechanical strain-induced mitogenesis in human vascular smooth muscle cells via down-regulation of Sp-1. Cardiovascular Research 50(1):108-114'' 2001.
215. Liu B'' Qu MJ'' Qin KR'' Li H'' Li ZK'' Shen BR'' Jiang ZL. Role of cyclic strain frequency in regulating the alignment of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro. Biophys J 94:1497-1507'' 2008.
216. Liu G'' Hitomi H'' Hosomi N'' Lei B'' Pelisch N'' Nakano D'' Kiyomoto H'' Ma H'' Nishiyama A. Mechanical stretch potentiates angiotensin II-induced proliferation in spontaneously hypertensive rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertens Res 33(12):1250-1257'' 2010. Epub 2010 Oct 7.
217. Liu X'' Hymel LJ'' Songu-Mize E. Involvement of intracellular Ca2+ and Na+ in stretch-regulated Na+'' K+-ATPase α isoform expression in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells [abstract]. FASEB J 11:A263'' 1526'' 1997.
218. Liu X'' Hymel LJ'' Songu-Mize E. Mechanosensitivity of Na+'' K+-ATPase α subunit expression in aortic smooth muscle cells [abstract]. Biophys J 70:A348'' Tu-Pos 497'' 1996.
FLEXCELL® INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
23
219. Liu X'' Hymel LJ'' Songu-Mize E. Role of Na+ and Ca2+ in stretch-induced Na+-K+-ATPase α-subunit regulation in aortic smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 274:H83–H89'' 1998.
220. Liu X'' Hymel LJ'' Songu-Mize E. Sodium entry through stretch-activated channels mediates upregulation of Na+'' K+-ATPase α isoforms in aortic smooth muscle cells [abstract]. Hypertension 30(Part 1):512'' P175'' 1997.
221. Lundberg MS'' Sadhu DN'' Grumman VE'' Chilian WM'' Ramos KS. Actin isoform and α1B-adrenoceptor gene expression in aortic and coronary smooth muscle is influenced by cyclical stretch. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 31(8):595-600'' 1995.
222. Mayr M'' Li C'' Zou Y'' Huemer U'' Hu Y'' Xu Q. Biomechanical stress-induced apoptosis in vein grafts involves p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases. FASEB J 14(2):261-270'' 2000.
223. Metzler B'' Abia R'' Ahmad M'' Wernig F'' Pachinger O'' Hu Y'' Xu Q. Activation of heat shock transcription factor 1 in atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol 162(5):1669-1676'' 2003.
224. Mills I'' Cohen CR'' Kamal K'' Li G'' Shin T'' Du W'' Sumpio BE. Strain activation of bovine aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation and alignment: study of strain dependency and the role of protein kinase A and C signaling pathways. J Cell Physiol 170(3):228-34'' 1997.
225. Mills I'' Murata K'' Packer CS'' Sumpio BE. Cyclic strain stimulates dephosphorylation of the 20kDa regulatory myosin light chain in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 205(1):79-84'' 1994. Erratum in: Biochem Biophys Res Commun 207(3):1058'' 1995.
226. Mohanty MJ'' Li X. Stretch-induced Ca2+ release via an IP3-insensitive Ca2+ channel. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283(2):C456-C462'' 2002.
227. Morawietz H'' Ma YH'' Vives F'' Wilson E'' Sukhatme VP'' Holtz J'' Ives HE. Rapid induction and translocation of Egr-1 in response to mechanical strain in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 84(6):678-687'' 1999.
228. Morrow D'' Scheller A'' Birney YA'' Sweeney C'' Guha S'' Cummins PM'' Murphy R'' Walls D'' Redmond EM'' Cahill PA. Notch-mediated CBF-1/RBP-Jκ-dependent regulation of human vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype in vitro. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 289(5):C1188-C1196'' 2005.
229. Morrow D'' Sweeney C'' Birney YA'' Cummins PM'' Walls D'' Redmond EM'' Cahill PA. Cyclic strain inhibits Notch receptor signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro. Circ Res 96(5):567-575'' 2005.
230. Morrow D'' Sweeney C'' Birney YA'' Guha S'' Collins N'' Cummins PM'' Murphy R'' Walls D'' Redmond EM'' Cahill PA. Biomechanical regulation of hedgehog signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro and in vivo. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292(1):C488-C496'' 2007.
231. Noda M'' Katoh T'' Takuwa N'' Kumada M'' Kurokawa K'' Takuwa Y. Synergistic stimulation of parathyroid hormone-related peptide gene expression by mechanical stretch and angiotensin II in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 269(27):17911-17917'' 1994.
232. Noda M'' Takuwa Y'' Katoh T'' Kurokawa K. Stretch-induced parathyroid hormone-related peptide gene expression: implication in the regulation of myogenic tone. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 4(5):383-387'' 1995.
FLEXCELL® INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
24
233. Numaguchi K'' Eguchi S'' Yamakawa T'' Motley ED'' Inagami T. Mechanotransduction of rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells requires RhoA and intact actin filaments. Circ Res 85(1):5-11'' 1999.
234. O’Callaghan CJ'' Williams B. Mechanical strain-induced extracellular matrix production by human vascular smooth muscle cells: role of TGF-β1. Hypertension 36(3):319-324'' 2000.
235. Putnam AJ'' Cunningham JJ'' Dennis RG'' Linderman JJ'' Mooney DJ. Microtubule assembly is regulated by externally applied strain in cultured smooth muscle cells. J Cell Sci 111(Pt 22):3379-3387'' 1998.
236. Pyle AL'' Atkinson JB'' Pozzi A'' Reese J'' Eckes B'' Davidson JM'' Crimmins DL'' Young PP. Regulation of the atheroma-enriched protein'' SPRR3'' in vascular smooth muscle cells through cyclic strain is dependent on integrin α1β1/collagen interaction. Am J Pathol 173(5):1577-1588'' 2008. Epub 2008 Oct 2.
237. Qu M'' Liu B'' Jiang Z. Effect of frequency of cyclic tensile strain on extracellular matrix of rat vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi 25(4):826-830'' 2008.
238. Qu MJ'' Liu B'' Qi YX'' Jiang ZL. Role of Rac and Rho-GDI α in the frequency-dependent expression of h1-calponin in vascular smooth muscle cells under cyclic mechanical strain. Ann Biomed Eng 36(9):1481-1488'' 2008. Epub 2008 Jun 20.
239. Qu MJ'' Liu B'' Wang HQ'' Yan ZQ'' Shen BR'' Jiang ZL. Frequency-dependent phenotype modulation of vascular smooth muscle cells under cyclic mechanical strain. J Vasc Res 44(5):345-353'' 2007. Epub 2007 May 3.
240. Rakugi H'' Yu H'' Kamitani A'' Nakamura Y'' Ohishi M'' Kamide K'' Nakata Y'' Takami S'' Higaki J'' Ogihara T. Links between hypertension and myocardial infarction. American Heart Journal 132(1 Pt 2 Su):213-221'' 1996.
241. Regnault V'' Perret-Guillaume C'' Kearney-Schwartz A'' Max JP'' Labat C'' Louis H'' Wahl D'' Pannier B'' Lecompte T'' Weryha G'' Challande P'' Safar ME'' Benetos A'' Lacolley P. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor: a new link among arterial stiffness'' pulse pressure'' and coagulation in postmenopausal women. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31(5):1226-1232'' 2011. Epub 2011 Feb 3.
242. Reusch P'' Wagdy H'' Reusch R'' Wilson E'' Ives HE. Mechanical strain increases smooth muscle and decreases nonmuscle myosin expression in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 79(5):1046-1053'' 1996.
243. Reyna SV'' Ensenat D'' Johnson FK'' Wang H'' Schafer AI'' Durante W. Cyclic strain stimulates L-proline transport in vascular smooth muscle cells. American Journal of Hypertension 17(8):712-717'' 2004.
244. Richard MN'' Deniset JF'' Kneesh AL'' Blackwood D'' Pierce GN. Mechanical stretching stimulates smooth muscle cell growth'' nuclear protein import'' and nuclear pore expression through mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J Biol Chem 282(32):23081-23088'' 2007. Epub 2007 May 24.
245. Ruiz-Velasco V'' Mayer MB'' Hymel LJ. Dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ influx modulated by stretch in A7r5 vascular smooth muscle cells. European Journal of Pharmacology 296(3):327-334'' 1996.
246. Schad JF'' Meltzer KR'' Hicks MR'' Beutler DS'' Cao TV'' Standley PR. Cyclic strain upregulates VEGF and attenuates proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Vasc Cell 3:21'' 2011.
FLEXCELL® INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
25
247. Sedding DG'' Hermsen J'' Seay U'' Eickelberg O'' Kummer W'' Schwencke C'' Strasser RH'' Tillmanns H'' Braun-Dullaeus RC. Caveolin-1 facilitates mechanosensitive protein kinase B (Akt) signaling in vitro and in vivo. Circ Res 96(6):635-642'' 2005.
248. Sedding DG'' Homann M'' Seay U'' Tillmanns H'' Preissner KT'' Braun-Dullaeus RC. Calpain counteracts mechanosensitive apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro and in vivo. FASEB J 22(2):579-589'' 2008. Epub 2007 Sep 10.
249. Sevieux N'' Alam J'' Songu-Mize E. Effect of cyclic stretch on α-subunit mRNA expression of Na+-K+-ATPase in aortic smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280(6):C1555-C1560'' 2001.
250. Sevieux N'' Alam J'' Songu-Mize E. Effect of cyclic stretch on transcriptional regulation of the α subunits of Na+'' K+-ATPase in aortic smooth muscle cells [abstract]. FASEB J 14:A331'' 272.5'' 2000.
251. Sevieux N'' Alam J'' Wiltse S'' Songu-Mize E. Expression of the α subunit mRNA of Na+'' K+-ATPase in response to cyclic stretch in aortic smooth muscle cells [abstract]. FASEB J 13:351.4'' 1999.
252. Sevieux N'' Ark M'' Hornick C'' Songu-Mize E. Short-term stretch translocates the α-1-subunit of the Na pump to plasma membrane. Cell Biochem Biophys 38(1):23-32'' 2003.
253. Shyu KG'' Chao YM'' Wang BW'' Kuan P. Regulation of discoidin domain receptor 2 by cyclic mechanical stretch in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension 46(3):614-621'' 2005.
254. Shyu KG'' Wang BW'' Kuan P'' Chang H. RNA interference for discoidin domain receptor 2 attenuates neointimal formation in balloon injured rat carotid artery. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28(8):1447-1453'' 2008. Epub 2008 May 22.
255. Songu-Mize E'' Jacobs M'' Shreves A. Acute cyclic stretch induces upregulation of the Na-pump of aortic smooth muscle cells in culture by cytoplasmic translocation [abstract]. FASEB J 13:351.5'' 1999.
256. Songu-Mize E'' Jacobs M. Effect of cyclic in vitro stretch on aortic smooth muscle cell p42 and p44 mitogen acticated kinases [abstract]. FASEB J 12(Part I):A403'' 2342'' 1998.
257. Songu-Mize E'' Liu X'' Hymel LJ. Effect of mechanical strain on expression of Na+''K+-ATPase α subunits in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Amer J Med Sci 316(3):196-199'' 1998.
258. Songu-Mize E'' Liu X'' Stones JE'' Hymel LJ. Regulation of Na+'' K+-ATPase α-subunit expression by mechanical strain in aortic smooth muscle cells. Hypertension 27:827-832'' 1996.
259. Songu-Mize E'' Liu X. Effect of cyclic mechanical strain on expression of Na+''K+-ATPase α subunits in rat aortic smooth muscle cells [abstract]. Cellular Deformation: Mechanics and Mechanisms of Physiological Response Meeting'' Atlanta GA'' October 1997.
260. Songu-Mize E'' Sevieux N'' Liu X'' Jacobs M. Effect of short-term cyclic stretch on sodium pump activity in aortic smooth muscle cells. Amer J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 281:H2072-H2078'' 2001.
FLEXCELL® INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
26
261. Standley PR'' Camaratta A'' Nolan BP'' Purgason CT'' Stanley MA. Cyclic stretch induces vascular smooth muscle cell alignment via NO signaling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283(5):H1907-H1914'' 2002.
262. Standley PR'' Obards TJ'' Martina CL. Cyclic stretch regulates autocrine IGF-I in vascular smooth muscle cells: implications in vascular hyperplasia. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 276:E697-E705'' 1999.
263. Standley PR'' Stanley MA'' Senechal P. Activation of mitogenic and antimitogenic pathways in cyclically stretched arterial smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 281(6):E1165-E1171'' 2001.
264. Stanley AG'' Knight AL'' Williams B. Mechanical strain sensitizes human vascular smooth muscle cells to angiotensin II. American Journal of Hypertension 13(4 Suppl 1):S12'' 2000.
265. Stanley AG'' Patel H'' Knight AL'' Williams B. Mechanical strain-induced human vascular matrix synthesis: the role of angiotensin II. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 1(1):32-35'' 2000.
266. Stones J'' Liu X'' Hymel L'' Songu-Mize E. Upregulation of Na+'' K+-ATPase α-1 subunit in aortic smooth muscle cells stretched in culture [abstract]. Hypertension 26:578'' P158'' 1995.
267. Su BY'' Shontz KM'' Flavahan NA'' Nowicki PT. The effect of phenotype on mechanical stretch-induced vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis. J Vasc Res 43(3):229-237'' 2006.
268. Sumpio BE'' Banes AJ'' Link WG'' Johnson G Jr. Enhanced collagen production by smooth muscle cells during repetitive mechanical stretching. Arch Surg 123(10):1233-1236'' 1988.
269. Sumpio BE'' Banes AJ. Response of porcine aortic smooth muscle cells to cyclic tensional deformation in culture. J Surg Res 44(6):696-701'' 1988.
270. Tamura K'' Chen YE'' Lopez-Ilasaca M'' Daviet L'' Tamura N'' Ishigami T'' Akishita M'' Takasaki I'' Tokita Y'' Pratt RE'' Horiuchi M'' Dzau VJ'' and Umemura S. Molecular mechanism of fibronectin gene activation by cyclic stretch in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 275(44):34619-34627'' 2000.
271. Tan W'' Scott D'' Belchenko D'' Qi HJ'' Xiao L. Development and evaluation of microdevices for studying anisotropic biaxial cyclic stretch on cells. Biomed Microdevices 10(6):869-882'' 2008.
272. Tock J'' Van Putten V'' Stenmark KR'' Nemenoff RA. Induction of SM-α-actin expression by mechanical strain in adult vascular smooth muscle cells is mediated through activation of JNK and p38 MAP kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 301(4):1116-1121'' 2003.
273. van Wamel AJ'' Ruwhof C'' van der Valk-Kokshoom LE'' Schrier PI'' van der Laarse A. The role of angiotensin II'' endothelin-1 and transforming growth factor-β as autocrine/paracrine mediators of stretch-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Mol Cell Biochem 218(1-2):113-124'' 2001.
274. van Wamel AJ'' Ruwhof C'' van der Valk-Kokshoorn LJ'' Schrier PI'' van der Laarse A. Stretch-induced paracrine hypertrophic stimuli increase TGF-β1 expression in cardiomyocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 236(1-2):147-153'' 2002.
FLEXCELL® INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
27
275. von Offenberg Sweeney N'' Cummins PM'' Birney YA'' Redmond EM'' Cahill PA. Cyclic strain-induced endothelial MMP-2: role in vascular smooth muscle cell migration. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 320:325–333'' 2004.
276. Walker-Caprioglio HM'' Hunter DD'' McGuire PG'' Little SA'' McGuffee LJ. Composition in situ and in vitro of vascular smooth muscle laminin in the rat. Cell Tissue Res 281(1):187-196'' 1995.
277. Wernig F'' Mayr M'' Xu Q. Mechanical stretch-induced apoptosis in smooth muscle cells is mediated by β1-integrin signaling pathways. Hypertension 41(4):903-911'' 2003.
278. Wiersbitzky M'' Mills I'' Sumpio BE'' Gewirtz H. Chronic cyclic strain reduces adenylate cyclase activity and stimulatory G protein subunit levels in coronary smooth muscle cells. Exp Cell Res 210(1):52-55'' 1994.
279. Wilson E'' Mai Q'' Sudhir K'' Weiss RH'' Ives HE. Mechanical strain induces growth of vascular smooth muscle cells via autocrine action of PDGF. J Cell Biol 123(3):741-747'' 1993.
280. Wilson E'' Vives F'' Collins T'' Ives HE. Strain-responsive regions in the platelet-derived growth factor-A gene promoter. Hypertension 31(1 Pt 2):170-175'' 1998.
281. Yang Z'' Noll G'' Luscher TF. Calcium antagonists differently inhibit proliferation of human coronary smooth muscle cells in response to pulsatile stretch and platelet- derived growth factor. Circulation 88:832-836'' 1993.
282. Zampetaki A'' Zhang Z'' Hu Y'' Xu Q. Biomechanical stress induces IL-6 expression in smooth muscle cells via Ras/Rac1-p38 MAPK-NF-κB signaling pathways. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288(6):H2946-H2954'' 2005.
Other cardiovascular cells
283. Balguid A'' Rubbens MP'' Mol A'' Bank RA'' Bogers AJ'' van Kats JP'' de Mol BA'' Baaijens FP'' Bouten CV. The role of collagen cross-links in biomechanical behavior of human aortic heart valve leaflets - relevance for tissue engineering. Tissue Eng 13(7):1501-1511'' 2007.
284. Boerboom RA'' Rubbens MP'' Driessen NJ'' Bouten CV'' Baaijens FP. Effect of strain magnitude on the tissue properties of engineered cardiovascular constructs. Annals of Biomedical Engineering 36(2):244–253'' 2008.
285. Clause KC'' Tinney JP'' Liu JL'' Keller BB'' Huard J'' Tobita K. p38MAP-kinase regulates cardiomyocyte proliferation and contractile properties of engineered early embryonic cardiac tissue [abstract]. Weinstein Cardiovascular Development Research Conference'' Indianapolis'' IN'' 2007.
286. Clause KC'' Tinney JP'' Liu LJ'' Keller BB'' Tobita K. Engineered early embryonic cardiac tissue increases cardiomyocyte proliferation by cyclic mechanical stretch via p38-MAP kinase phosphorylation. Tissue Engineering Part A 15(6):1373-1380'' 2009.
287. Foolen J'' Baaijens F. Stress-fiber remodeling in 3D: ‘contact guidance vs stretch avoidance’? QScience Proceedings vol. 2012'' Heart Valve Biology and Tissue Engineering'' pp. 62'' 2012. doi: 10.5339/qproc.2012.heartvalve.4.62
288. Gupta V'' Grande-Allen KJ. Effects of static and cyclic loading in regulating extracellular matrix synthesis by cardiovascular cells. Cardiovasc Res 72(3):375-383'' 2006. Epub 2006 Sep 1.
FLEXCELL® INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
28
289. Kapur NK'' Deming CB'' Kapur S'' Bian C'' Champion HC'' Donahue JK'' Kass DA'' Rade JJ. Hemodynamic modulation of endocardial thromboresistance. Circulation 115(1):67-75'' 2007.
290. Klein G'' Schaefer A'' Hilfiker-Kleiner D'' Oppermann D'' Shukla P'' Quint A'' Podewski E'' Hilfiker A'' Schroder F'' Leitges M'' Drexler H. Increased collagen deposition and diastolic dysfunction but preserved myocardial hypertrophy after pressure overload in mice lacking PKCε. Circ Res 96(7):748-755'' 2005.
291. Ku CH'' Johnson PH'' Batten P'' Sarathchandra P'' Chambers RC'' Taylor PM'' Yacoub MH'' Chester AH. Collagen synthesis by mesenchymal stem cells and aortic valve interstitial cells in response to mechanical stretch. Cardiovasc Res 71(3):548-556'' 2006. Epub 2006 Apr 7.
292. Rakesh K'' Yoo B'' Kim IM'' Salazar N'' Kim KS'' Rockman HA. β-Arrestin-biased agonism of the angiotensin receptor induced by mechanical stress. Sci Signal 3(125):ra46'' 2010.
293. Throm Quinlan AM'' Sierad LN'' Capulli AK'' Firstenberg LE'' Billiar KL. Combining dynamic stretch and tunable stiffness to probe cell mechanobiology in vitro. PLoS ONE 6(8): e23272'' 2011. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0023272.
294. Tobita K'' Garrison JB'' Keller BB. Differential effects of cyclic stretch on embryonic ventricular cardiomyocyte and non-cardiomyocyte orientation. Edited by Clark EB'' Nakazawa M'' Takao A. Blackwell Futura Publishing:177-179'' 2005.
295. Tobita K'' Liu LJ'' Janczewski AM'' Tinney JP'' Nonemaker JM'' Augustine S'' Stolz DB'' Shroff SG'' Keller BB. Engineered early embryonic cardiac tissue retains proliferative and contractile properties of developing embryonic myocardium. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291(4):H1829-37'' 2006.
美国Flexcellint国际公司,成立于1987年,该公司专注于细胞力学培养产品的设计和制造。以提供独特的体外细胞拉应力、压应力和流体剪切应力加载刺激系统以及配套的培养板、硅胶膜载片等耗材闻名于世。
Flexcell的细胞组织体外机械力加载装置的细胞力学加载方法和能模拟生命体内细胞组织生长生物力环境、实现体外分离和建立合适的加载膜型公认国际领先''详见应用案例文献库
Flexcell细胞组织力学培养系统不仅能对各种2D、3D细胞组织提供拉应力、压应力、切应力刺激加载,而且还可以提供拉应力和切应力混合力同时加载;不仅能对细胞组织进行机械力加载刺激,而且还能三维培养、人工生物组织构建、动力模拟;不仅能单轴向牵张拉伸,而且还可以双轴向牵张拉伸。
Flexcell独具的StageFlexer拉应力显微设备、StagePresser压应力显微设备、Flex Flow切应力显微设备;这些显微设备可在加力培养的同时实时观察研究细胞组织反应变化;独具的flexstop隔离阀能使同一块培养板里的细胞组织一部分受力,一部分不受力,方便进行对比实验
这些系统智能、精准诱导来自各种细胞、组织在拉力、压力和流体切应力作用下发生的生化生理变化,专业、细腻的阐释了体外细胞、组织机械力刺激加载、力学信号感受和响应机制。对研究细胞的形态结构及功能,细胞的生长、发育、成熟、增殖、衰老、凋亡、死亡及癌变以及通路表达,细胞信号传导及基因表达的调控,细胞的分化及其调控机理具有重要意义。
| 口腔 |
颞下颌关节滑膜细胞、人牙周膜细胞、口腔上皮细胞、口腔鳞癌KB细胞等 |
| 骨: |
骨骼细胞、肌腱细胞、韧带细胞、软骨细胞和骨细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞,软骨组织、椎间盘骨组织、肌腱组织、韧带组织等 |
| 肺呼吸 |
肺细胞、肺上皮细胞、肺动脉内皮细胞、人肺微血管内皮细胞 |
| 眼科视觉神经 |
眼上皮细胞、眼小梁组织细胞、视网膜神经细胞 |
| 心血管/高血压: |
心肌细胞、血细胞、心血管平滑肌细胞、血管内皮细胞 |
| 生殖 |
肾膀胱细胞、平滑肌细胞/尿路上皮及尿路上皮细胞、肾小管上皮细胞 |
| 消化 |
肠上皮细胞、 胃上皮细胞、胃血管内皮细胞 |
| 皮肤 |
皮肤细胞、皮肤成纤维细胞 |
| Flexcell模块化的拉应力、压应力、切应力、三维培养模块,可任意组合统一主机多功能平台 |
1、FX-5000T细胞牵张拉伸应力加载系统(Flexcell FX5000 Tension system)
1)该系统对二维、三维细胞和组织提供轴向和圆周应力加载;
2)基于柔性膜基底变形、受力均匀;
3)可实时观察细胞、组织在应力作用下的反应;
4)独具的flexstop隔离阀可使同一块培养板力的一部分培养孔的细胞受力,一部分培养孔的细胞不受力,方便对比实验;
5)与压力传导仪整合,同时兼备多通道细胞压力加载功能;
6)与Flex Flow平行板流室配套,可在牵拉细胞的同时施加流体切应力;
7)多达4通道,可4个不同程序同时运行,进行多个不同拉伸形变率对比实验;
8)同一程序中可以运行多种频率,多种振幅和多种波形;
9)更好地控制在超低或超高应力下的波形;
10)多种波形种类:静态波形、正旋波形、心动波形、三角波形、矩形以及各种特制波形;
11)电脑系统对牵张拉伸力加载周期、大小、频率、持续时间精确智能调控
12)加载分析各种细胞在牵张拉应力刺激下的生物化学反应
13)伸展度:0-33%
14)牵拉频率:0.01-5Hz
2、FX-5000C细胞压力加载系统(flexcell FX5000 Compression system)——提供样机体验

1)该系统对各种组织、三维细胞培养物提供周期性或静态的压力加载;
2)基于柔性膜基底变形、受力均匀;
3)可实时观察细胞、组织在压力作用下的反应;
4)可有选择性地封阻对细胞的应力加载;
5)同时兼备多通道细胞牵拉力加载功能;
6)多达4通道,可4个不同程序同时运行,进行多个不同压力形变率对比实验;
7)同一程序中可以运行多种频率(0.01- 5 Hz),多种振幅和多种波形;
8)更好地控制在超低或超高应力下的波形;
9)多种波形种类:静态波形、正旋波形、心动波形、三角波形、矩形以及各种特制波形;
10)电脑系统对压力加载周期、大小、频率、持续时间精确智能调控
11)检测各种组织和细胞在压力作用下的生物化学反应
12)压力范围:0.1 - 14磅
3、TissueTrain可拉伸组织工程三维细胞培养系统(Flexcell TissueTrain System)——提供样机体验
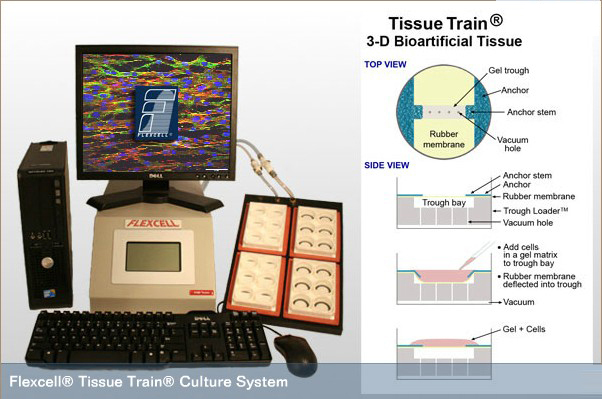
| FLEXCELL Tissue Train® 是个独立的全自动细胞组织三维培养、组织构建计算机智能控制的生物反应器系统,它允许研究者创建三维基质凝胶支架, |
| 在基质里细胞培养、构建生物组织,可为三维细胞、组织提供双轴向应力和单轴向应力,FLEXCELL Tissue Train® |
| 是当今科研界最先进的可拉伸刺激三维细胞培养、生物组织构建系统系统。 |
系统功能亮点:
- 三维细胞牵张应力加载刺激:对生长在三维状态下的细胞进行静态的或者周期性的拉应力刺激
通过Flexcell应力加载系统和弧矩形加载平台对生长在三维环境下的细胞进行单轴向
或者双轴向的静态或者周期性的应力加载刺激培养
- 三维细胞培养:使用三维组织培养模具和三维细胞培养板可以进行三维细胞培养在凝胶支架里全自动三维培养
三维组织培养模具和三维细胞培养板类型丰富:
1)三维组织培养模具有三维线形培养加载基站模具和三维梯形培养加载基站模具
2)具有氨基酸包被表面、胶原(I型或IV)包被表面、弹性蛋白包被表面、ProNectin(RGD)包被表面、层粘连蛋白(YIGSR)包被表面的三维培养板。
科研者根据自己的细胞,有针对性的选择适合包被表面三维培养板
3)具有可牵拉双轴向和单轴向拉力刺激加载三维组织培养板。
- 大体积三维生物人工组织培养构建:可构建长度达35mm的生物人工组织
- 动力模拟实验:可建立特制的各种模拟实验:心率模拟实验、步行模拟实验、跑动模拟实验和其他动力模拟实验
- 本系统技术先进性:
1)安全快速的扩增细胞
2)在细胞特异性基质(圆盘形陶瓷载体培养片) 中进行三维的细胞高密度培养
3)扩增并获得可用于治疗的有活性的原代细胞
4)在控制分化状态的条件下扩增干细胞
5)向植入的一代细胞提供植入支架
6)长期培养分泌细胞
7)高效生产重组蛋白和疫苗
8)生产优质的糖蛋白
9)三维培养与机械力刺激有机结合
10)三维凝胶压实自动测量与面积自动计算
- 可用于多个领域,如研究、生物制药加工;也可为细胞和组织培养工作提供解决方案:
1)可用于干细胞和胚体扩增及定向分化
2)可用于细胞和组织治疗的细胞制备
3)可用于克隆细胞,为器官移植做准备(例如hip stem'' heart valve'' graft)
4)可用于制备天然的生物制品(例如糖蛋白、病毒、病毒样颗粒)
- 观察细胞应力下实时反映:使用Flexcell独有的Flexcell StageFlexer Jr.显微附属设备,可在加力刺激的同时实时观察细胞在三维状态下牵拉刺激的反应
- 多种基质蛋白包被的尼龙网锚可以加强细胞与网锚的结合
|
4、STR-4000细胞流体切应力系统(Flexcell Fluid Shear Stress Device)——提供样机体验
4.1、六通道流体切应力加载分析设备—Streamer剪切力设备
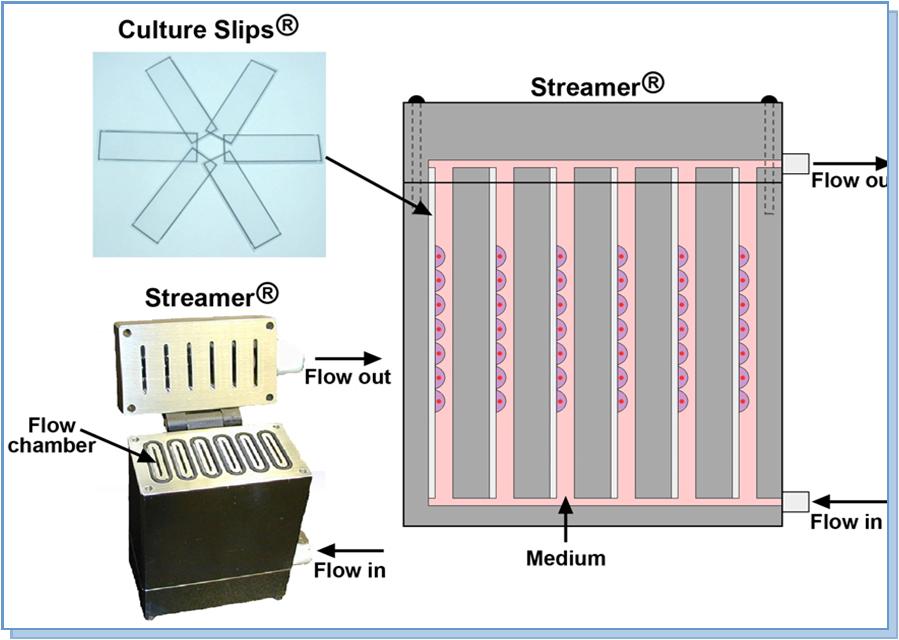
- 为细胞提供各种形式的流体切应力:稳流式切应力、脉冲式切应力或者往返式切应力。
- 在经过特殊基质蛋白包被的25x 75x 1.0mm细胞培养载片上培养细胞。
- 多达6通道,每个通道放不同载片,可培养不同的细胞
- 计算机控制的蠕动泵可以调节切应力大小从0-35 dynes/cm2
- 通过Osci-Flow液体控制仪提供往返式或脉冲式流体切应力。
- 检测细胞在液流作用下的排列反应。
- 设备易拆卸并可高温消毒。
- 可以在经过特殊包被的6个细胞培养载片上同时培养细胞。
- 提供两个液流脉冲阻尼器。
Streamer System产品包括:
1)Streamer设备;
2) DELL笔记本式计算机;
3)快拆接头及胶管;
4)蠕动泵;
5)StreamSoft软件;
6)2个液流脉冲阻尼器;
7)12个细胞培养载片(Culture Slip)
4.2、HiQ Flowmate纳升和微微液流控制双注射系统

- 双注射泵可以在微升,纳升和微微升水平上控制液流.双注射泵,独立的液流控制系统。
- 传送精确,稳定的流速
- 可控流速范围1.2pL/ min-260.6ml/min
- 提供不同流速模型:稳定型,脉冲型,连续型,截流型和震荡型;
- 可进行循环,连续的液流控制;同时运行不同的流速模型;
- 内置阀门控制液流模式;
- 机载计算器用于流量、流时、流速、剪切力的计算;
- 高分辨率、触屏控制。
- 用户友好的图标驱动程序;
- 便于泵和芯片对接的生物芯片支架;根据现有流速有三种不同的机型;
多种应用程序:
- 液体稀释,配给及注射器;
- 动物实验中的药物注射和体液抽取;
- 施加液流剪切力;
- 微流体和纳流体实验;
- 混合、分流液体;
- 震荡型液流的控制需要iHIQ Flowmate二级阀门配件
4.3 Osci-Flow切应力模式控制器——完美的液流控制模式


- 通过计算机控制提供可调控的,往返式的或者脉冲式的流体切应力。
- 和Streamer及FlexFlow shear stress设备一起使用。
- 维持泵的流速不''最大限度的降低改变泵的转速引起的流液的延反应迟。
- 可以在瞬间内改变流体流动方向。
- 兼容其它公司生产的灌流系统。
- 兼容各种类型MasterFlexL/S系列或者相应的胶管。
- 通过PC板卡可以和绝大多数便携式计算机连接使用。
- Osci-Flow装置DAQ Card DIO-24说明书和NI-DAQ软件
- 连接Osci-Flow和板卡的缆线;
- DELL电脑需单独购买
- 胶管和快拆接头;StreamSoft软件;
5、Flexflow平行板流室系统提供流体切应力同时抻拉细胞
FlexcellFlexFlow显微切应力加载设备(SHEAR Stress device)